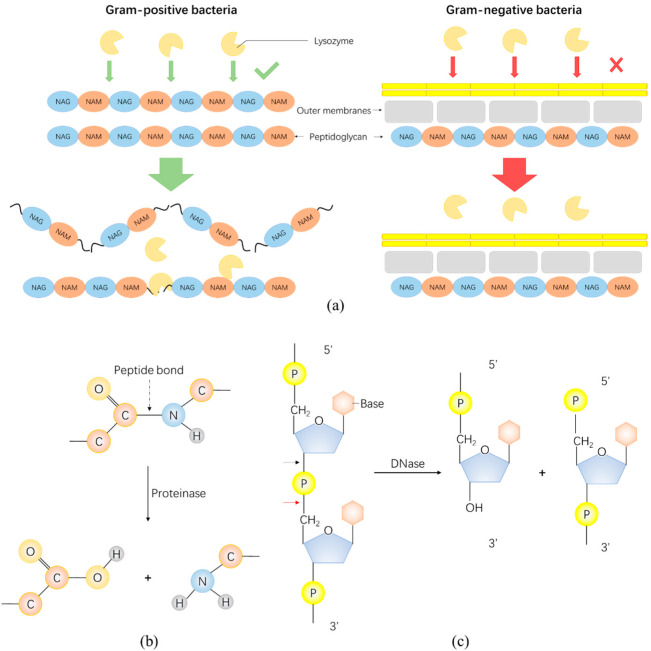
Figure 2.
Schematic of the antibacterial mechanism of several typical enzybiotics. (a) Schematic of the action of the lysozyme on Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. (b) Proteinase can degrade proteins by hydrolyzing peptide bonds. (c) Nuclease mainly consists of DNase and RNase, which degrade DNA and RNA, respectively. This figure uses DNase hydrolysis of phosphodiester bound as an example. The black arrow is the hydrolysis site of DNase and the red arrow is the hydrolysis site of RNase (e.g., RNase A family).