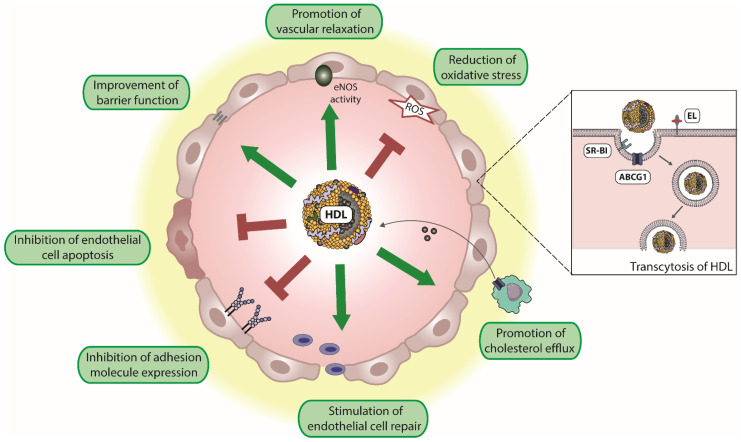
Figure 1.
Endothelium-protective activities of HDL. HDL particles exert several protective effects on the endothelium, including reduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), the improvement of endothelial barrier function, and promotion of vascular relaxation by increasing endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activity. Moreover, HDL inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis, suppresses the expression of endothelial adhesion molecules, and stimulates endothelial cell repair. In addition, HDL promotes reverse cholesterol transport, by uptake of cholesterol from macrophages and other peripheral cells. Transendothelial transport of HDL is mediated by scavenger receptor B1 (SR-BI), ATP-binding cassette G1 (ABCG1), and endothelial lipase (EL).