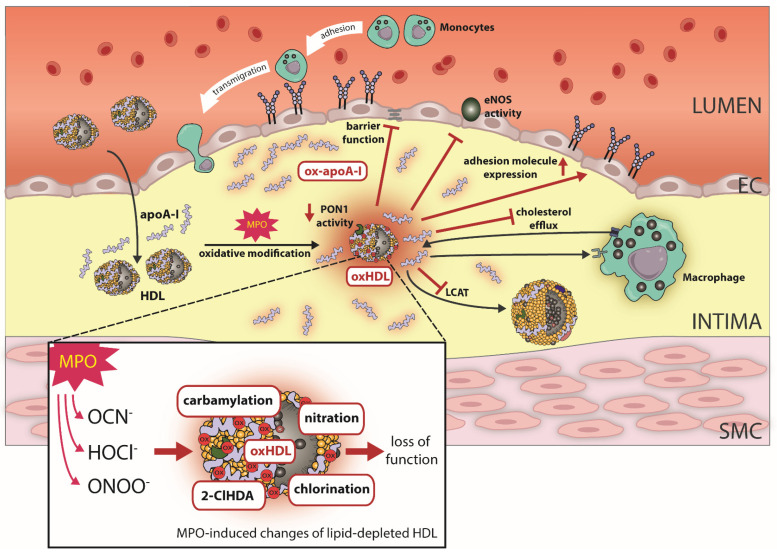
Figure 2.
Effect of MPO-induced oxidative modifications on HDL function. In the atherosclerotic vessel wall, HDL/apoA-I is a target for MPO-catalyzed oxidation. Specifically, the MPO products hypochlorus acid (HOCl−), cyanate (OCN−) and peroxynitrite (ONOO−) lead to chlorination, carbamylation, nitration and the formation of the plasmalogen oxidation product 2-Chlorohexadecanal (2-ClHDA). Oxidative modifications of HDL by MPO results in loss of HDL’s ability to activate endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS). Moreover, MPO modified HDL compromises endothelial barrier function and upregulates endothelial adhesion molecule expression. Further, MPO-catalyzed oxidation of HDL impairs cholesterol efflux capacity via ABCA1, whereas affinity for SR-BI increases. MPO also targets PON1 and leads to decreased activity. Oxidative modifications of apoA-I result in a profoundly decreased activity of LCAT. ApoA-I, apolipoprotein A1; MPO, myeloperoxidase; ABCA1, ATP-binding cassette transporter A1.