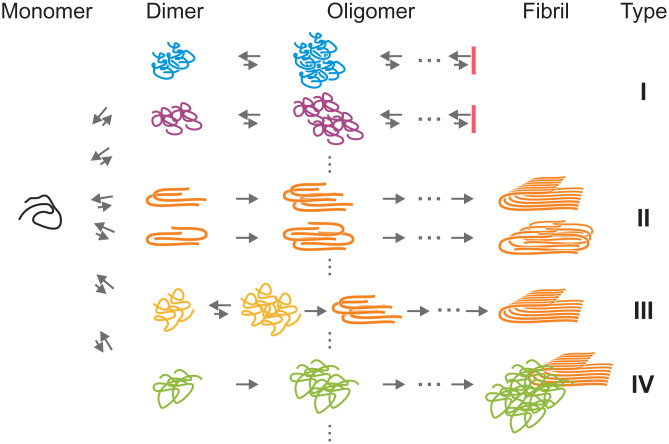
Fig. 6.
Model of heterogeneous Aβ42 oligomerization and aggregation. Initially, monomers form dimers or small oligomers with different structures, which are followed by diverse oligomerization and aggregation pathways. In type I pathways, the assembly stops in oligomeric stages. Type II and III pathways lead to fibril elongation, but the stage where fibril-like conformations are formed is different for the two types (see Discussion). Type III requires conformational conversion from non-β structures to cross-β structures. There are fibrils growing on the surface of oligomers with different structures (heterogeneous secondary nucleation, type IV pathway). The heterogeneity observed in the experiment suggests that multiple different pathways exist in each type of aggregation pathways indicated by vertical dots.