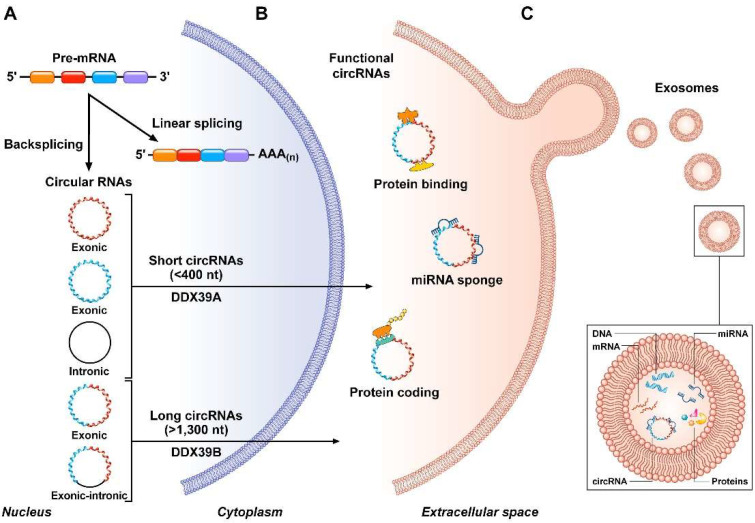
Figure 1.
CircRNA biogenesis and functions. (A) Circularization of circRNAs, including exonic, intronic, and exonic-intronic circRNAs, arises from pre-mRNA transcripts through different mechanisms of back-splicing. After formation, circRNAs are transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm by RNA helicases (DDX39A, or DDX39B) in a size-dependent manner. (B) CircRNAs have different mechanisms of action. Indeed, they can interact with proteins, encode for proteins, and function as microRNA sponge (mainly). (C) CircRNAs can be further released into body fluids as cell-free circRNAs or enriched in extracellular vesicles (e.g., exosomes).