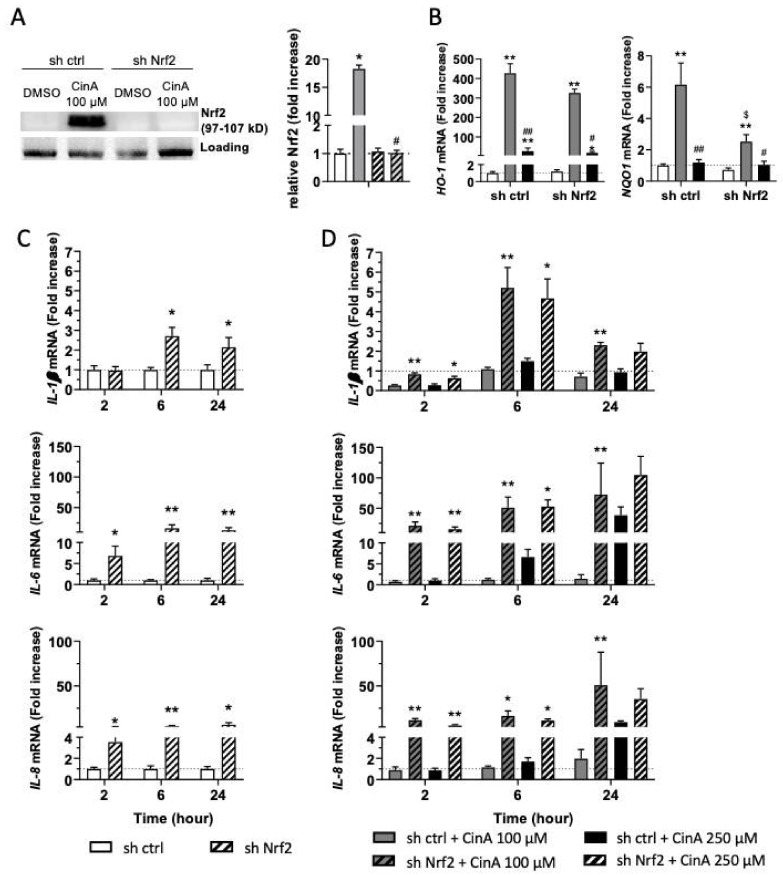
Figure 4.
The control of the inflammatory in response to CinA is Nrf2-dependent. KCs were invalidated for Nrf2 by transduction with lentiviral particles to express a short-hairpin RNA targeting Nrf2 (sh Nrf2) or a scrambled short-hairpin (sh ctrl) as the control cells, and the cells were exposed to 100 or 250 µM of CinA from 2 to 24 h. (A) Western blot and relative quantification of Nrf2 after exposure to CinA or DMSO 0.1% as the vehicle control for 6 h. Representative of 4 independent experiments. (B) mRNA levels of HO-1 and NQO1 measured by RT-qPCR after 6 h of exposure to 100 or 250 µM of CinA and DMSO 0.1% as the vehicle control. (C) mRNA level of inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 determined by RT-qPCR after 2, 6, and 24 h of culture without any stimulation. (D) mRNA levels of inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 determined by RT-qPCR after 2, 6, and 24 h of exposure to 100 or 250 µM of CinA. Data represent the results of 5 independent experiments and are expressed as the mean ± SEM. (A,B) * Represents the statistical difference between CinA and vehicle-treated cells, # represents the statistical difference between 100 µM and 250 µM-treated cells, and $ represents the statistical difference between sh ctrl and sh Nrf2 cells. (C,D) * Represents the statistical difference between sh ctrl and sh Nrf2 cells. *, # p-value < 0.05 and **, ## p-value < 0.01 (Mann–Whitney test).