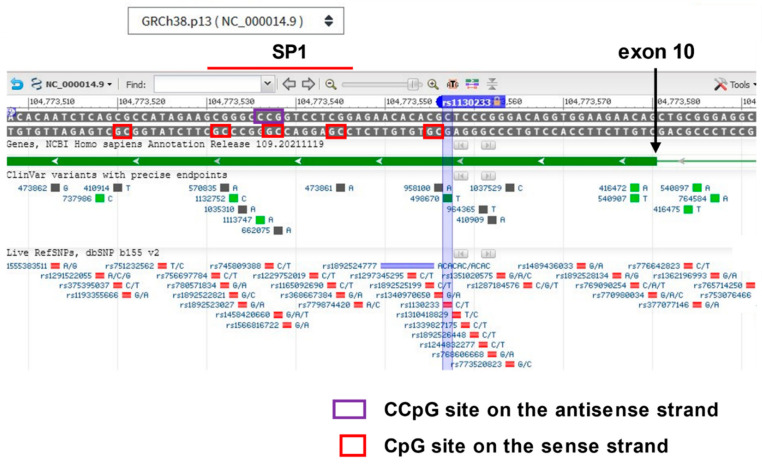
Figure 4.
Screenshot of exon 10 of the AKT1 gene on the NCBI gene map for chromosome 14, intended to illustrate the power of NCBI data available, including the panoply of SNPs shown below, most very rare. Note the reverse orientation of the gene. Hovering a cursor over exon 10 (shown in dark green) will allow access to the FASTA nucleotide and protein sequence for the entire gene. Location of rs1130233 is shown relative to downstream CpG sites identified by Blest- Blest-Hopley et al. [117] to be differentially methylated in correlation with degree of THC-induced regional human brain activation in response to a fearful cue. The chromosomal location given in their paper for two sites found to be most significantly differentially methylated, chr14: 104,773,527–104,773,522, does not correspond to any two adjacent CpG sites separated by 5 bp. However, just upstream are two methylation sites separated by 5 bp, are part of a binding site for the expression-enhancing transcription factor SP1, according to the in silico analysis tool Alibaba2. Binding of SP1 within an exon is known to occur for other genes [128,129,130]. SP1 binding is generally not affected by methylation, except when the sites are immediately outside the binding motif [64] or include double methylation to yield mCmCpG inside the binding motif on the antisense strand [119,120]. In these scenarios, SP1 binding is inhibited by methylation, and expression of the transcript may be similarly affected. Blest-Hopley et al. [117] did not make clear if the cg probes they utilized would pick up mCmCpG. Regardless, the global hypomethylation of AKT1 associated with smoking may well act to restore SP1 binding in exon 10.