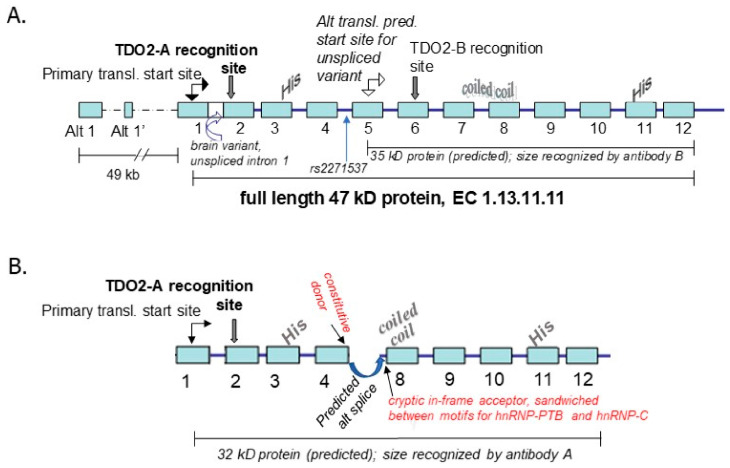
Figure 6.
Isoforms of TDO2 in the brain, recognized by antibodies directed to different epitopes, TDO2-A and TDO2-B; the specificity of antibody A for TDO2 confirmed by Schmidt et al. [164] in a Western blot of recombinant human TDO2. Epigenetic regulation of these isoforms is likely. (A). Experimental evidence derived from sequencing a cDNA clone of a brain transcript that retained intron 1, supports the existence of isoform TDO2-B, as two ORF finding programs (™DNAstar, NCBI) revealed this intron-1-retained sequence shifts the predicted start site to an ATG in exon 5; the resulting protein would be 35 kD as seen in the Western blots. The location of the SNP for a genetic association study, rs2271537 [65] is indicated. (B). In silico prediction of one potential identity for TDO2-A. As the post-translational modifications of TDO2 have to-date been shown to be limited to phosphorylation of 6 residues (see dbPTM), the maximum likely kD difference between the predicted isoform from in silico analysis and the actual isoform in vivo is likely limited to <0.5 kD. Analysis of constitutive and cryptic donor/acceptor pairs by the program ASSP identified a single continuous ORF (confirmed by the program Augustus and the NCBI ORF identifier) that would match the 32 kD protein size recognized by TDO2-A, spliced as shown from a constitutive donor at the end of exon 4 to an in-frame cryptic acceptor—gactattaat—identified by the ASSP program in the 3-prime region of intron 7. Surrounding this 5′ acceptor site lie two motifs for alternative-splicing-repressors identified by the program Alibaba2, hnRNP-PTB (CTCTCT) and hnRNP-C (TTTTT), substantiating this site as an important regulatory point [186]. The missing sequence would modify the active site, as would the substitution of the in-frame aa sequence QTINAIFFLKA from intron 1. Note retention of the histidine (HIS) residue coded by exon 3 and a tryptophan residue coded by exon 11 which are thought to be important for holding the 5-membered ring of tryptophan in the active site, along with a phenylalanine coded by exon 3 (via interacting with the aromatic ring of tryptophan), whereas the heme is bound by histidine coded for in exon 11, a tyrosine coded in exon 6, and a glycine coded in exon 6 [187]. The coiled coil region coded in exon 8, thought to be important for tetramer formation [188], was predicted by both ™DNAstar and WAGGA).