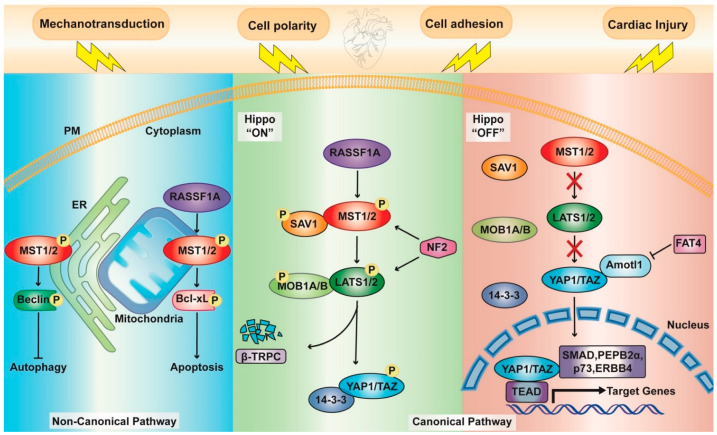
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the key components of the Hippo pathway. Canonical Pathway: In the “on” active state (central panel), upstream kinases (MST1/2, LATS1/2) together with their cofactors (SAV1 and MOB1A/B, respectively) are phosphorylated. Subsequential phosphorylation of YAP1/TAZ engages either 14-3-3 proteins for cytoplasmic retention or β-TrCP for ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation. In the “off” inactive state (right panel), upstream kinases are inactive; thus, YAP1/TAZ can translocate to the nucleus and bind with multiple transcription factors, including TEADs, SMAD, PEPB2α, P73, and ERBB4, thereby regulating several genes. The central components of the hippo pathway are regulated by several mechanisms and proteins, such as NF2, Amotl1, and FAT4. Noncanonical pathway (left panel): MST1 can directly phosphorylate either Beclin 1 at the ER, inhibiting autophagy in cardiomyocytes, or negatively regulating Bcl-xL at the mitochondria, enhancing cardiomyocyte apoptosis.