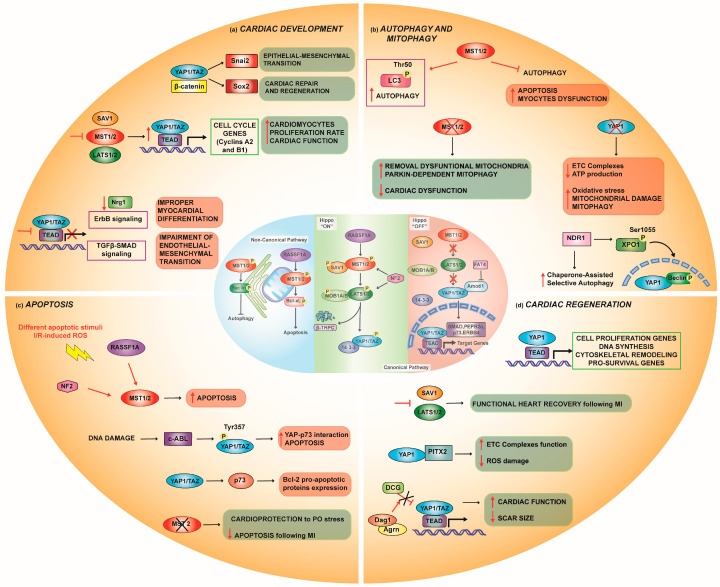
Figure 2.
The Hippo pathway in cardiovascular physiology. (a) YAP1 expression is involved in cardiac development: the Wnt/β-catenin pathway synergically works with YAP1 to induce cardio genesis; nuclear YAP1 mediates cell cycle genes (cyclins A2 and B1), prompting cardiomyocyte proliferation; and YAP1 loss inhibits either ErbB or TGF-β-SMAD signaling with consequent improper myocardial development. (b) Hippo signaling controls autophagy and mitophagy: MST1/2 enhance autophagic flux through LC3 phosphorylation at Thr50; in contrast, under pathological conditions, MST1/2 both inhibits autophagy and boosts apoptosis. However, melatonin mediates autophagy activation through inhibiting MST1/2 phosphorylation and enhancing Parkin-dependent mitophagy. NDR1 kinase induces autophagy by YAP1 and Beclin1 translocation into the nucleus through XPO1 phosphorylation and modulates chaperone-assisted selective autophagy. Doxorubicin downregulates YAP1, leading to cardiac damage, which is the cause of activation of both autophagy and mitophagy. (c) Under pathological conditions, such as I/R, MST1/2 kinases are activated, leading to cardiomyocyte apoptosis; cytosolic YAP1 is stabilized by c-Abl phosphorylation at Tyr357, thus enhancing the YAP1-P73 interaction to activate apoptosis. (d) Inhibition of upstream kinases of the Hippo pathway, such as LATS1/2, promotes YAP1 nuclear translocation, thus targeting gene expression for cell proliferation and heart regeneration. YAP1 cardiac regenerative function is enhanced either by PITX2, which cooperatively reduces ROS damage, or by the Argn-Dag1 complex, which pulls apart DCG and improves cardiac function.