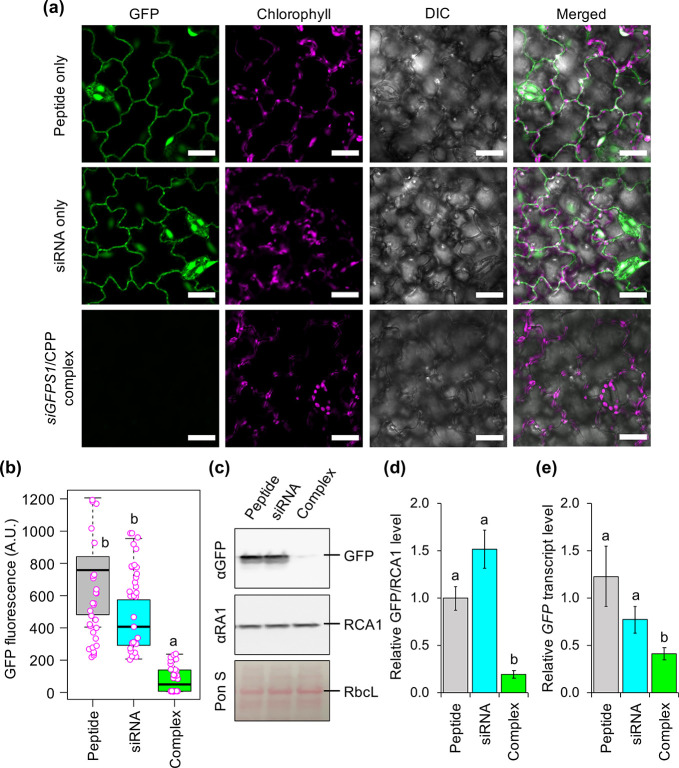
Figure 5.
Transgene suppression in tomato leaves mediated by spraying with siRNA/CPP complexes. (a) CLSM images of epidermal cells of transgenic tomato leaves overexpressing GFP after spraying with siGFPS1/KH9-BP100 complexes at 3 days after spraying (DAS). Scale bars = 20 μm. (b) Distribution of GFP fluorescence intensities in leaves sprayed with siRNA/CPP complexes at 3 DAS. Data points (magenta circles) of GFP fluorescence analyzed from CLSM images by ImageJ are shown in a box plot (n = 30 ROIs, 10 ROIs per leaf, three independent experiments), and black bars represent the median values. (c) Immunoblot analysis of GFP and RCA1 (endogenous plant protein control) in tomato leaves sprayed with KH9-BP100 only (P), siGFPS1 only (S), and siGFPS1/KH9-BP100 complex formed at N/P ratio = 2.0 (C). The membrane was stained by Ponceau S (Pon S) to confirm equal protein loading, as indicated by the RbcL bands on the membrane. (d) Quantitative analysis of GFP accumulation in transgenic tomato leaves sprayed with siRNA/CPP complex. Relative GFP/RCA1 protein levels were analyzed from three experimentally independent immunoblot membranes by ImageJ. Error bar = standard deviation (SD). (e) Transcript suppression in leaves after spraying with siRNA/CPP complex. GFP transcript levels in three independent tomato leaves were analyzed by qRT-PCR at 3 DAS. Error bar = SD. Significant differences among treatments in panels b, d, and e analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD test at p = 0.05 are indicated by different letters in the graphs.