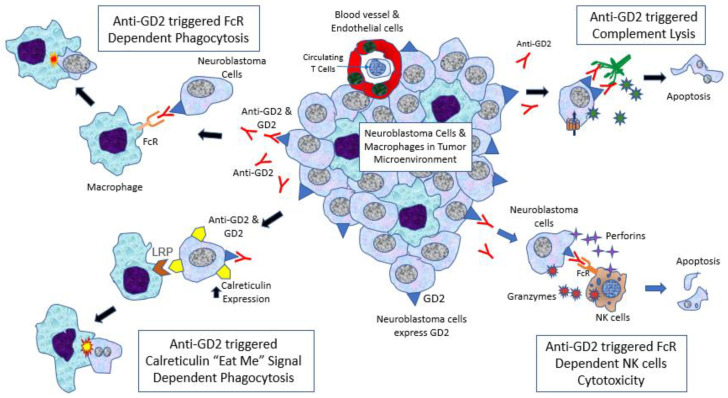
Figure 2.
Neuroblastoma tumor microenvironment and cytotoxic action induced by anti-GD2. (1) Anti-GD2 can trigger complementary activation by C1q–antibody interaction, leading to complement lysis of neuroblastoma cells (complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC)). (2) Anti-GD2 activates natural killer (NK) cells via FcγRIIIA (CD16a), leading to release of perforins and granzymes that can kill neuroblastoma cells (antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC)). (3) Anti-GD2 can activate macrophages via FcγRI (CD64) and FcγRIIA (CD32), leading to initiation of phagocytosis of neuroblastoma cells (antibody-dependent phagocytosis (ADP)). (4) Monoclonal antibodies such as anti-GD2 can induce calreticulin (“eat me” molecule) expression on neuroblastoma cells and enhance phagocytosis by macrophages.