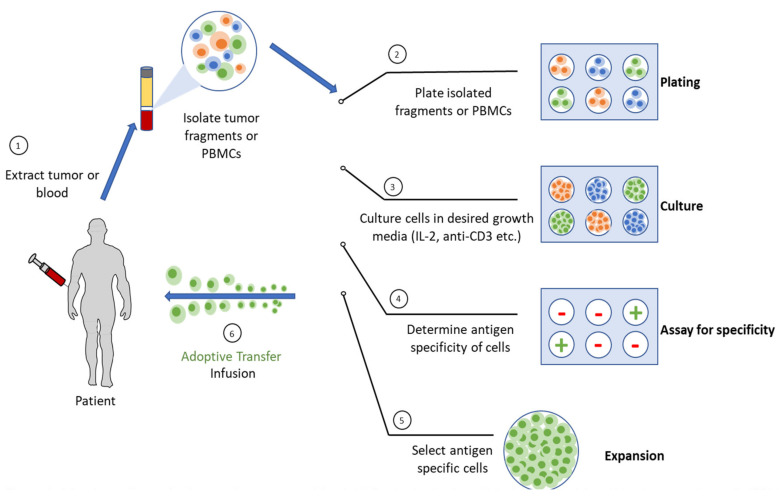
Figure 1.
Adoptive cell transfer from patient tumor or blood. (1) Production begins with isolation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from leukapheresis or tumor is excised and multiple individual cultures are isolated and (2) plated separately followed by (3) selection and activation of T cells. (4) T cells then undergo genetic modification for generating CAR-T cells or tumor cultures are assayed for specific tumor recognition. (5) Cells are expanded in presence of interleukins and when desired dose cell numbers are achieved, expanded cells are harvested and dose is formulated. (6) QC tests are performed to ensure that drug meets release criteria and is then fused into patients with or without conditioning lymphodepleting chemotherapy (6).