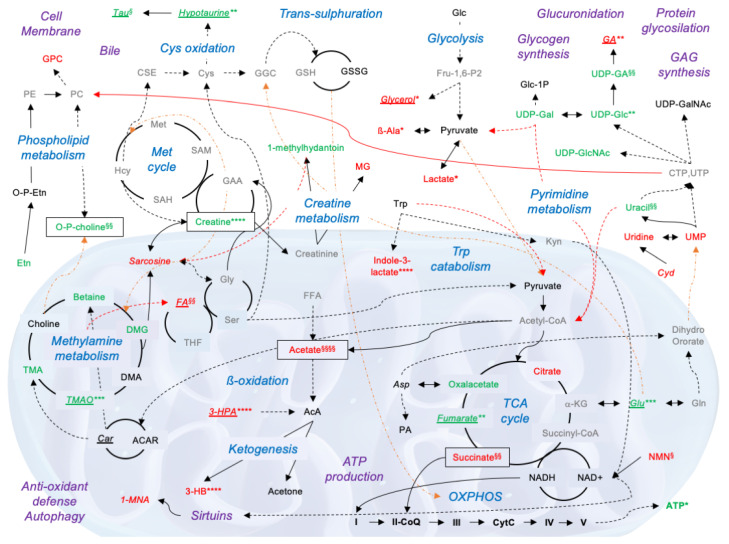
Figure 6.
Simplified diagram showing the metabolomic pathways modulated during normothermic machine perfusion (NMP) and their interactions. Metabolites typed in red fonts are upregulated in the NMP groups compared to the Native group, while those typed in green fonts are downregulated. Metabolites typed in black fonts had a similar concentration across ex vivo perfused and native livers. Metabolites detected only in perfusate sample are typed in italics, those detected only in bile samples are in italics and underlined. Metabolites which were undetectable by NMR-based spectroscopy are indicated in gray fonts. Differences across experimental groups were investigated by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. p-values are indicated as follows: all the NMP groups vs. Native: * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001; only OxC-NMP vs. Native: § p < 0.05; §§ p < 0.01; §§§§ p < 0.0001. Black arrows indicate a direct relationship between two metabolites; black dotted arrows denote multiple enzyme reactions to convert one metabolite into another; red arrows link one specific metabolic pathway to a different pathway; orange dotted arrows indicate metabolite translocation from mitochondria to cytoplasm and vice versa. Adapted from KEGG reference pathways. Abbreviations: I, NADH dehydrogenase; II, NADH dehydrogenase; III, cytochrome C reductase; IV, cytochrome C oxidase; V, ATP synthase; 1-MNA, 1-methylnicotinamide; 3-HB, 3-hydroxybutyrate; 3-HPA, 3-hydroxyphenylacetate; α-KG, α-ketoglutarate; AcA, acetoacetate; ACAR, acetylcarnitine; ATP, Adenosine triphosphate; Ala, alanine; Asn, asparagine; Asp, aspartate; CoQ, coenzyme Q; Cyd, cytidine; CPT, cytidine-5′-triphosphate; CSE, cystathionine; CytC, cytochrome C; DMG, N,N-dimethylglycine; Etn, ethanolamine; FA, formic acid; FFA, free fatty acid; Fru-1,6-P2, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; GAA, guanidinoacetate acid; GAG, glycosaminoglycans; GGC, γ-glutamylcysteine; Glc, glucose; Gln, glutammine; Glu, glutammate; Gly, glycine; GPC, glycerophosphocholine; GSH, reduced glutathione; GSSG, glutathione disulfide (oxidized form); Hcy, homocysteine; IMP, inosine 5′-monophosphate; Kyn, kynurenine; MG, methylguanidine; NMN, nicotinamide ribotide; o-P-choline, O-phosphocholine; o-P-Etn, o-phosphoethanolamine; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; PA, pantothenic acid; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PCr, phosphocreatine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; Ser, serine; Tau, taurine; TGL, triglycerides; THF, tetrahydrofolate; TMA, trimethylamine; TMAO, trimethylamine N-oxide; UDP-GlcNAc, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine; UDP-Gal, UDP-galactose; UTP, uridine-5′-triphosphate; UDP-Glc, uridine diphosphate-glucose; UDP-GalNAc, UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine.