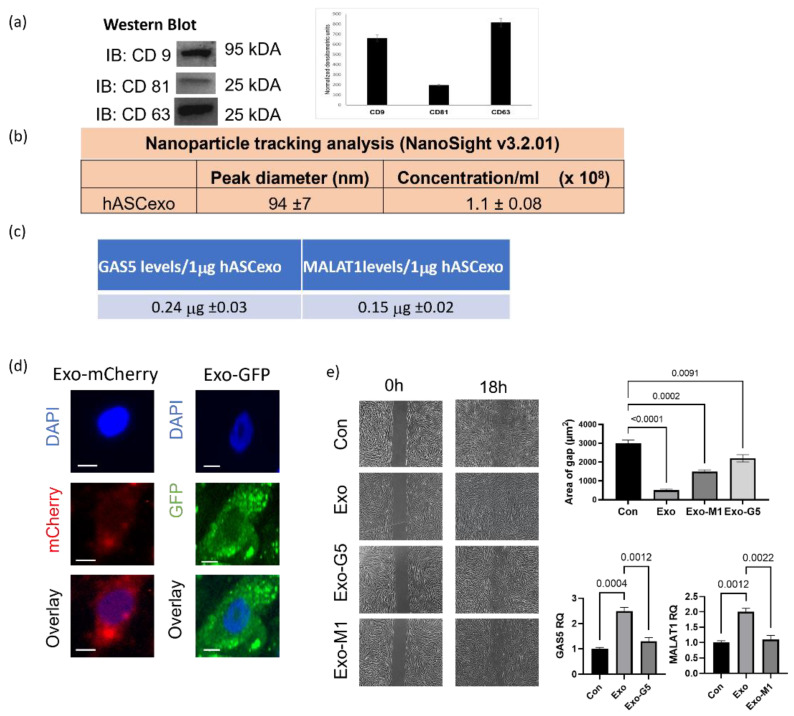
Figure 1.
Exosomes isolated from hASCs were verified by (a) western blot for hASC exosomal tetraspanin markers using antibodies against CD9, CD63, and CD81. The bands are representative of results obtained from experiments repeated five times. The graph represents ±SEM densitometric units. (b) The size and purity od hASC exosomes were evaluated using NanoSight v3.2.01 and (c) levels of long noncoding RNAs GAS5 and MALAT1 by absolute quantification by qPCR per 1 µg of exosomes across batches. (d) 1µg of mCherry or GFP overexpression plasmids were transfected into hASCs and exosomes were isolated from conditioned media. HDF cells were treated with 1 µg of exosomes and imaged using the Keyence microscope after 24 h showing uptake of hASC exosomes carrying mCherry or GFP (scale bar 20 µm, n = 3). (e) HDF cells were grown in a 35mm plate with Ibidi μ-inserts to generate consistent gaps. Inserts were removed and HDF cells were treated with exosomes (Exo) or exosomes depleted of GAS5 (Exo-G5) or depleted of MALAT1 (Exo-M1). Gap was imaged at time 0 and re-imaged after 18 hours. Wound gap was measured using Image J and area was calculated in µm2 (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA and significant p-values (<0.05) are indicated on graph.