Figure 1.
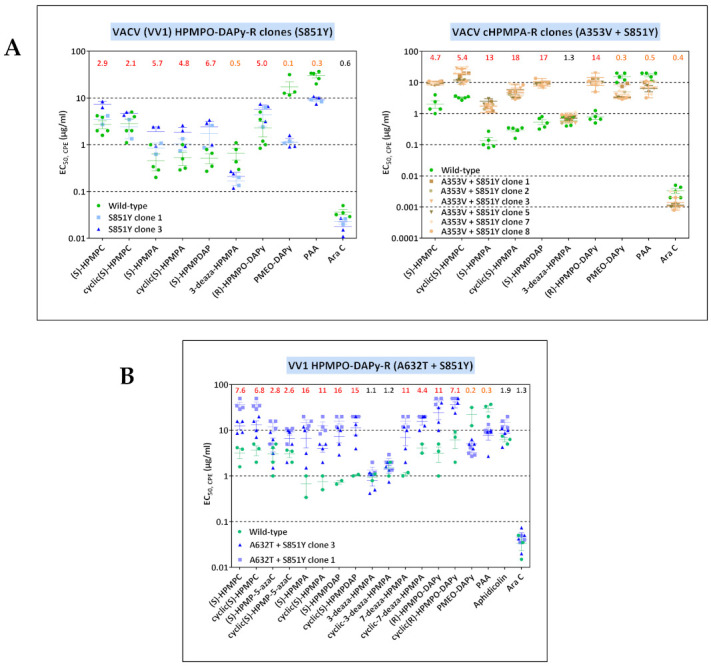
(A) Drug-susceptibility profile of cHPMPA-R VACV clones (A353V + S851Y) compared to VACV clones bearing the single S851Y DNA pol change recovered from VV1 HPMPO-DAPy-R #15. Drug-resistance properties of different plaque-purified viral clones bearing the single amino acid (S851Y) or double amino acid (A353V + S851Y) substitutions as determined using a CPE reduction assay with HEL fibroblasts. (B) Drug-susceptibility profile of selected VV1 HPMPO-DAP-R viral clones to evaluate the impact of the A632T + S851Y DNA polymerase substitutions. The A632T + A684V clones were recovered from VV1 HPMPO-DAPy-R #32. Drug-resistance properties of the different types of viral clones were established using a CPE reduction assay with HEL fibroblasts. The effects of different drugs on viruses encoding the indicated mutations were determined by calculating the EC50 values for the parental wild-type strain and clones bearing the specific mutations. At least two independent experiments were performed for each test compound. Horizontal lines for each drug and mutant viral clones indicate the mean values ± standard deviation. The fold resistance (ratio of the EC50 for the mutant viruses to the EC50 for the corresponding wild-type virus is marked at the top of the graph. VACV viral clones showing a ≥2-fold increase (red, bold) were considered drug resistant (R) and those with a ≤0.5-fold decrease (orange, bold) drug hypersensitive (hs).
