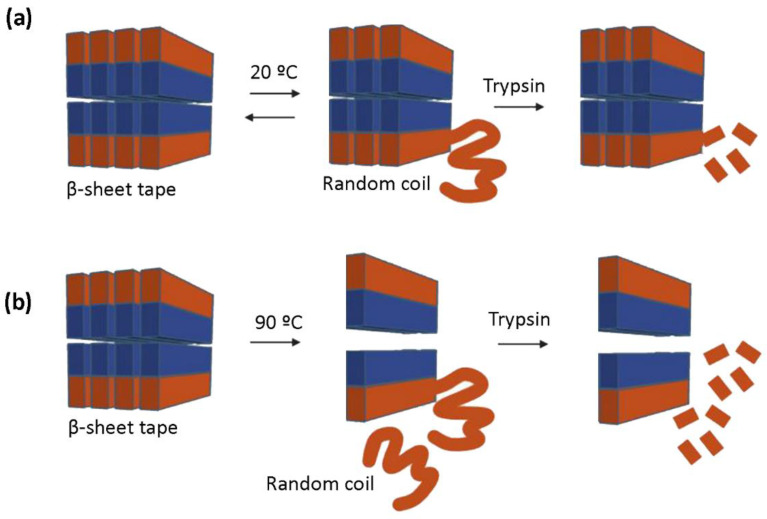
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of the model for the tryptic degradation of untreated and thermally treated RAD16-I samples. (a) Terminally located peptides are in equilibrium between β-sheet and random coil structure; (b) Thermal treatment accelerates this structural transition, in which the random coil peptide molecules are dissociated from the fiber ending and, thus, becoming susceptible to trypsin cleavage. On the contrary, peptides located in the stable fiber structure are inaccessible to the enzyme.