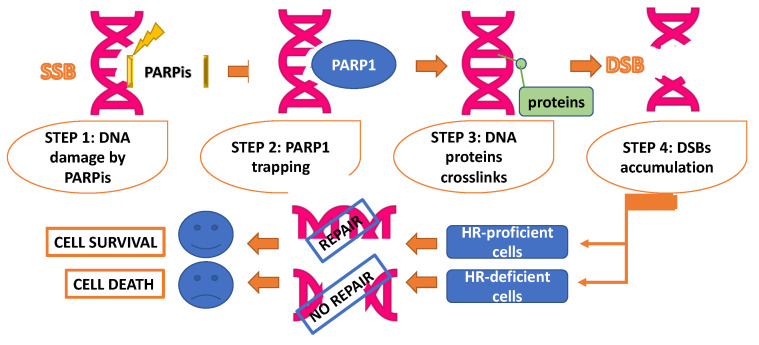
Figure 1.
Mechanism of action of polyADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors. Step 1: DNA damage caused by PARP inhibitors, with consequent creation of single strand DNA break (SSB); Step 2: detection of SSB by PARP1; Step 3: production of DNA protein crosslinks; Step 4: collapse of replication forks and double strand DNA breaks (DSBs) accumulation. While in homologous recombination (HR)-proficient cells these errors are restored by HR system, in HR-deficient tumor cells this process finally results in cell death.