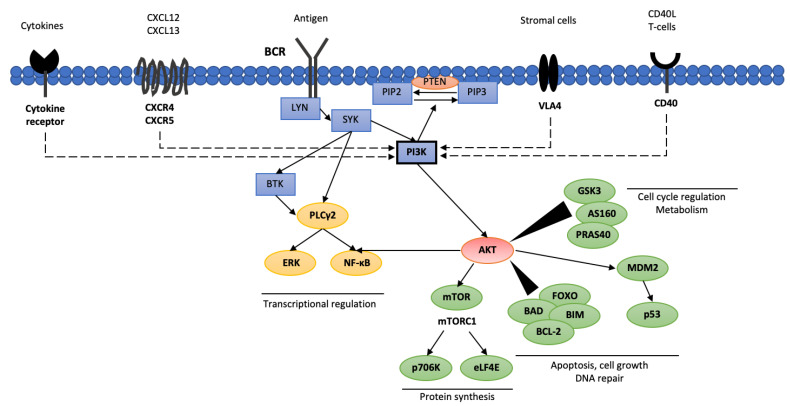
Figure 1.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases interacting pathways in CLL cells. AKT—protein kinase B (PKB); AS160—Akt substrate of 160 kDa; BCL-2—B cell lymphoma 2; BIM—bcl-2-interacting mediator of cell death; BAD—BCL2 associated agonist of cell death; BCR—B cell receptor; BTK—Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; CXCL12—C-X-C motif chemokine 12; CXCL13—C-X-C motif chemokine 13; eLF4E—eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E; ERK—extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FOXO—forkhead box protein; GSK3—glycogen synthase kinase 3; LYN—tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn; MDM2—mouse double minute 2 homolog; NF-κB—nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; p706K—p706 kinase; PI3K—phosphoinositide 3-kinases; PIP2—phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PIP3—phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate; SYK—spleen tyrosine kinase; PLCγ2—phospholipase C γ2; PTEN—phosphatase and tensin homolog; mTOR—mammalian target of rapamycin; PRAS40—proline-rich Akt substrate of 40 kDa; VLA4—very late antigen 4.