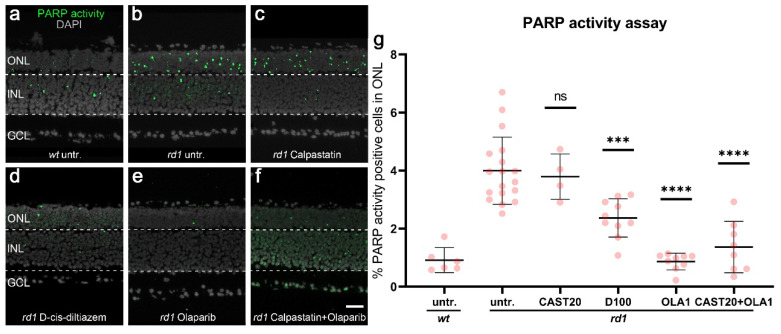
Figure 2.
Effects of calpastatin, D-cis-diltiazem, Olaparib, and combination treatments on PARP activity. PARP activity assay (green) in wt and rd1 retina. DAPI (grey) was used as nuclear counterstaining. Untreated wt (untr.; a) was compared to untreated rd1 retina (b) and retinae treated with either calpastatin (c), D-cis-diltiazem (d), Olaparib (e), or calpastatin and Olaparib combined (f). The scatter plots show the percentages of the outer nuclear layer (ONL) cells positive for PARP activity (g) in wt and rd1 retina. Statistical significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison post hoc testing performed between the control (rd1 untreated) and 20-μM calpastatin (CAST20), 100-μM D-cis-diltiazem (D100), 1-μM Olaparib (OLA1), and 20-μM calpastatin combined with 1-μM Olaparib (CAST20+OLA1). Calpastatin did not reduce the PARP activity, while D-cis-diltiazem and Olaparib did. Untr. wt: 6 explants from 3 different mice; untr. rd1: 18/18; CAST20 rd1: 4/4; D100 rd1: 10/10; OLA1 rd1: 9/9; CAST20+OLA1 rd1: 8/8; error bars represent SD; ns = p > 0.05, *** = p ≤ 0.001, and **** = p ≤ 0.0001. INL = inner nuclear layer, GCL = ganglion cell layer. Scale bar = 50 µm.