Scheme A1.
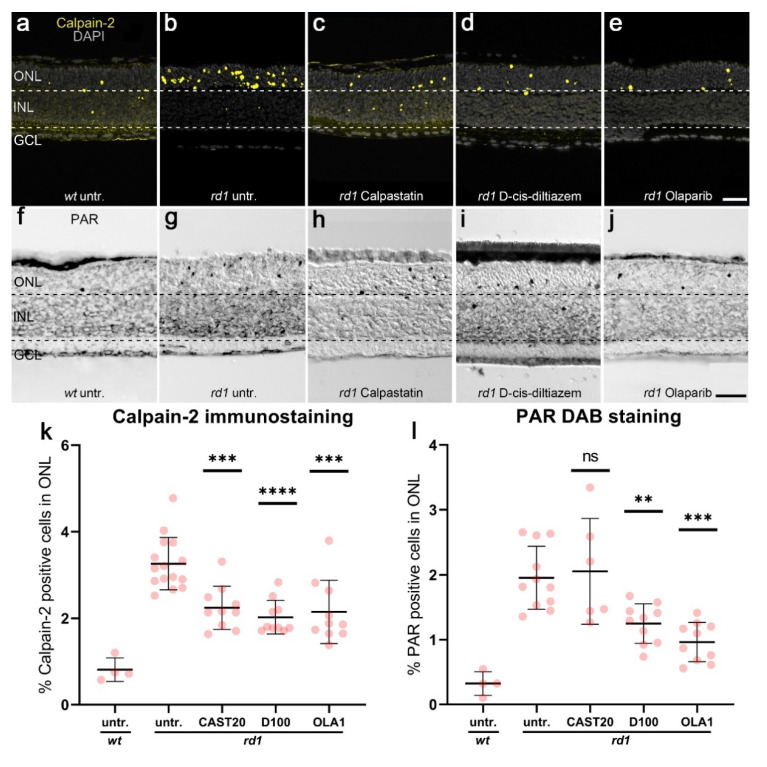
Effects of calpastatin, D-cis-diltiazem, and Olaparib on calpain-2 activation and PAR. Calpain-2 immunostaining (yellow; a–e) and PAR DAB staining (black, f–j) were performed on wt and rd1 retina. DAPI (grey) was used as nuclear counterstaining. Untreated rd1 retina (untr.; b,g) was compared to retina treated with calpastatin (c,h), D-cis-diltiazem (d,i), and Olaparib (e,j), respectively. The scatter plots show the percentages of ONL-positive cells for calpain-2 (k) and PAR (l) in wt and treated rd1 retina, compared with rd1 control (untr.). Statistical significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA, and Tukey’s multiple comparison post hoc testing was performed between the control and 20-μM calpastatin (CAST20), 100-μM D-cis-diltiazem (D100), and 1-μM Olaparib (OLA1). In rd1 retina, all treatments decreased the numbers of cells positive for calpain-2, while the number of PAR-positive cells were not reduced by CAST20. In calpain-2 immunostaining: Untr. wt: 4 explants from 2 different mice; untr. rd1: 15/15; CAST20 rd1: 10/10; D100 rd1: 10/10; OLA1 rd1: 10/10. In PAR DAB staining: untr. wt: 4/2; untr. rd1: 16/16; CAST20 rd1: 6/6; D100 rd1: 10/10; OLA1 rd1: 10/10; error bars represent SD; ns = p > 0.05, ** = p ≤ 0.01, *** = p ≤ 0.001, and **** = p ≤ 0.0001. ONL = outer nuclear layer, INL = inner nuclear layer, GCL = ganglion cell layer. Scale bar = 50 µm.