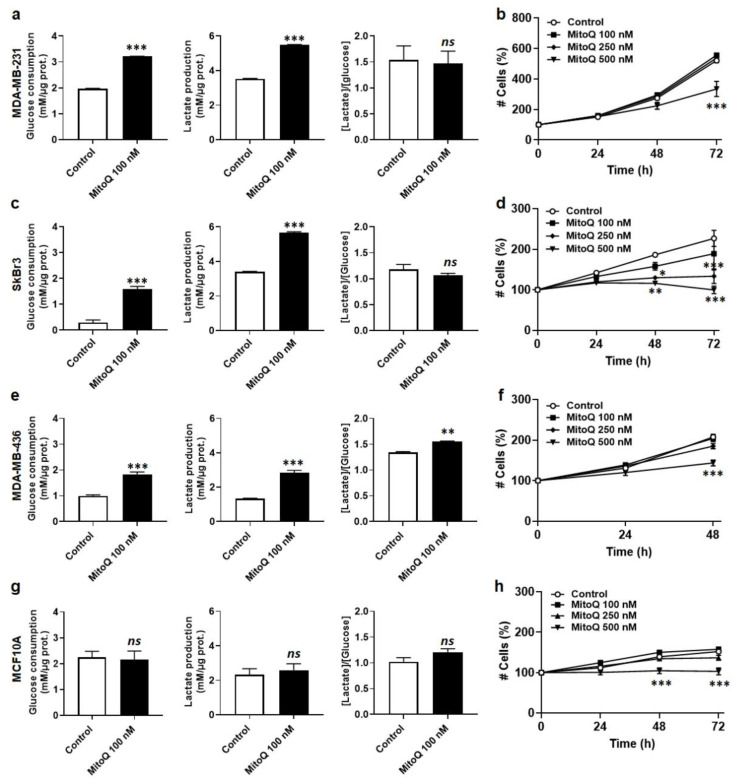
Figure 3.
MitoQ increases glucose consumption and lactate release by human breast cancer cells, and is cytostatic at doses ≥ 250 nM. (a) MDA-MB-231 cells were treated ± MitoQ 100 nM for 48 h. Glucose consumption (left), lactate production (middle) and the lactate/glucose ratio (right) were then determined using enzymatic assays on a CMA600 analyzer (n = 3 all). (b) Viable MDA-MB-231 cells were counted on a SpectraMax i3 spectrophotometer at the indicated time points after treatment with increasing doses of MitoQ (n = 4). (c) Enzymatic measurements of glucose and lactate consumption as in a, but using SkBr3 cells (n = 10). (d) SkBr3 cell viability was determined as in b (n = 8). (e) Enzymatic measurements of glucose and lactate consumption as in a, but using MDA-MB-436 cells (n = 10). (f) MDA-MB-436 cell viability was determined as in b (n = 8). (g) Enzymatic measurements of glucose and lactate consumption as in a, but using MCF10A normal epithelial breast cells (n = 4). (h) MCF10A cell viability was determined as in b (n = 8). All data are shown as means ± SEM. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 compared to control; ns: p > 0.05 compared to control; by Student t-test (a,c,e,g) or 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test (b,d,f,h).