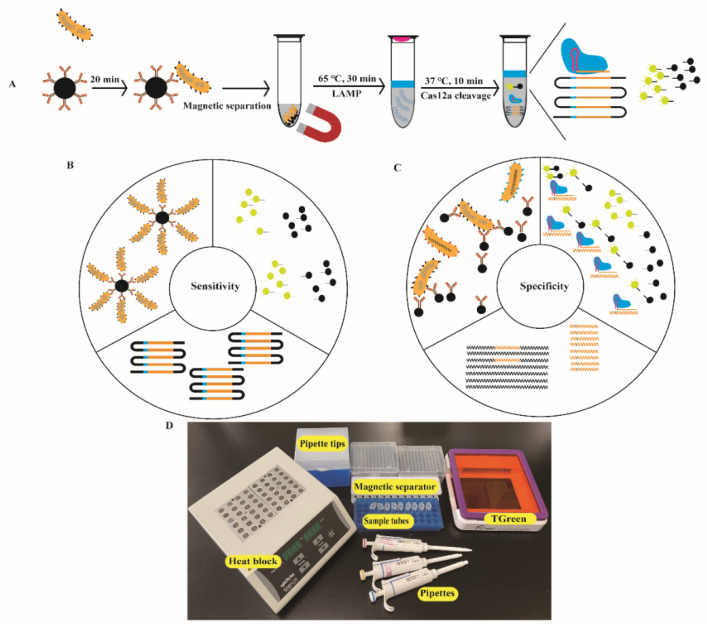
Figure 1.
Design and working principle of the ICB-LAMP-CRISPR/Cas12a method. (A) Schematic of the ICB-LAMP-CRISPR/Cas12a method. Campylobacter jejuni was captured by the prepared ICB and separated magnetically. Five microliters of template DNA of C. jejuni was added to the LAMP mixture, which was placed at the bottom of the tube and sealed with 20 μL of mineral oil. The CRISPR/Cas12a reaction reagents are added inside the lid. After 30 min of LAMP amplification at 65 °C, the tube was shaken to mix with Cas12a reagents for cleavage. Once the Cas12a nuclease is activated by recognizing the DNA target, it splits the quenched fluorescent ssDNA-FQ probe indiscriminately, generating a fluorescence signal visible to the naked eye under blue light. (B) Enhanced sensitivity of the ICB-LAMP-CRISPR/Cas12a method. The sensitivity was enhanced in three parts: the enrichment of ICB, the high efficiency of LAMP amplification, and the indiscriminate cleavage of the fluorescent ssDNA-FQ probe. (C) Enhanced specificity of the ICB-LAMP-CRISPR/Cas12a method. The specificity was enhanced from three parts: the specific antibodies of C. jejuni coated in the magnetic beads, the LAMP primers designed based on the conserved hipO gene, and the cleavage activity of Cas12a guide by the specific sgRNA. (D) Work conditions of the nearly instrument-free POC diagnostics. Equipment and consumables needed for running the ICB-LAMP-CRISPR/Cas12a method include a heat block, pipettes, pipette tips, sample tubes, and T-green transilluminator.