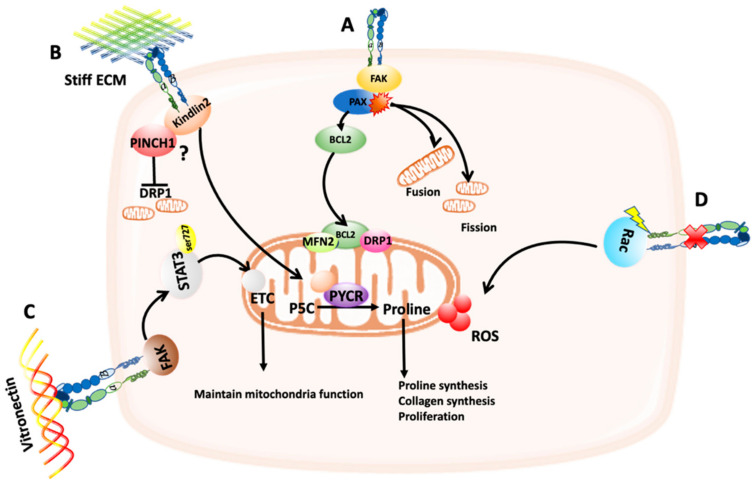
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the effect of cell/extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion on mitochondria function and dynamics. (A) Mutated forms of paxillin (PAX) have been shown to associate with BCL2, which in turn localizes to the mitochondria and interact with DRP1 and MFN2. In addition, mutations in PAX can cause changes in mitochondria fission and fusion. (B) PINCH1/kindlin2 interaction can affect DRP1 expression, therefore preventing mitochondria fission. Stiff ECM can trigger the translocation of kindlin2 to the mitochondria, where it interacts with PYCR1, increasing proline synthesis, collagen synthesis, and cell proliferation. (C) Binding of αvβ3 integrin to its ligand vitronectin can trigger FAK-dependent phosphorylation of STAT3 at Ser727, which promotes STAT3 translocation to the mitochondria, where it interacts with ETC complexes, maintaining mitochondria function. (D) Blocking α5β1 integrin results in Rac activation, which cause an increase in ROS induction.