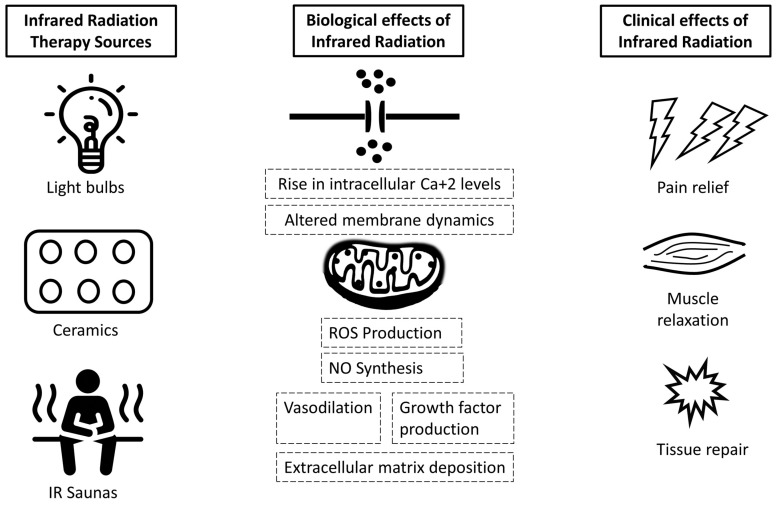
Figure 1.
Schematic presentation of IR therapy means of treatment and hypothesized biological and clinical effects with a focus on the musculoskeletal system. Briefly, exposure to infrared radiation leads to an intracellular increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) and a subsequent rise in nitric oxide (NO) synthesis and calcium intracellular levels (Ca2+). Eventually, this decreases oxidative stress, induces vasodilation and stimulates growth factor production and extracellular matrix deposition leading to tissue repair. Abbreviations: reactive oxygen species: ROS, nitric oxide: NO, calcium: Ca2+.