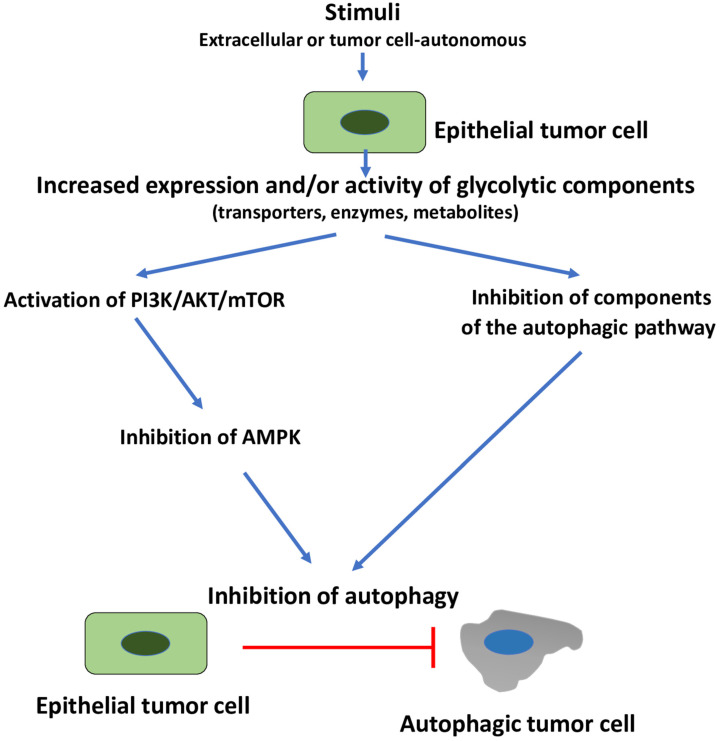
Figure 3.
Glycolysis-induced autophagy inhibition. Stimuli, either tumor cell-autonomous or from the TME (extracellular) increase the expression and/or activity of one or more glycolytic components (transporters, enzymes or metabolites). This can lead to activation of several signaling pathways. One of these pathways is the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway which leads also to AMPK inhibition and, consequently, to autophagy inhibition. Autophagy inhibition can occur also due to an inhibitory interaction of a glycolytic enzyme with components of the autophagy pathway. AMPK, adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; EMT, epithelial–mesenchymal transition; PI3K/AKT/mTOR, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/mechanistic target of rapamycin.