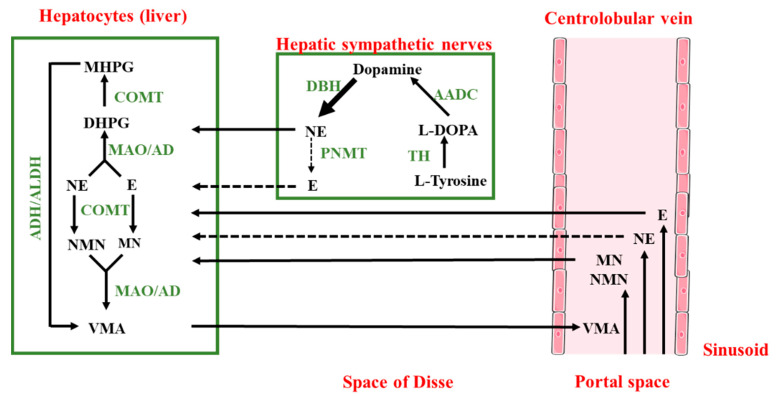
Figure 1.
Metabolism of epinephrine (E) and norepinephrine (NE) in the liver. Adrenal glands, mesenteric organs, and liver sympathetic innervation are the main sources of E and NE in the liver. The last step of metabolism for metanephrine (MN) and normetanephrine (NMN) extracted from the circulation are also performed in the liver. Thus, E, NE, MN, and NMN are uptaken by hepatocytes and metabolized in VMA. VMA is then eliminated in the urine. AD: aldehyde reductase; ADH: alcohol dehydrogenase; ALDH: aldehyde dehydrogenase; MAO: monoamine oxidases; COMT: catechol-O-methyltransferase; TH: tyrosine hydroxylase; AADC: aromatic L-aminoacid decarboxylase; DBH: dopamine-β-hydroxylase; PNMT: phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase; DHPG: 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycol; MHPG: 4-hydroxy-3methoxyphenylglycol; VMA: vanillyl mandelic acid (Solid arrow: main pathway; dotted arrow: minor pathway).