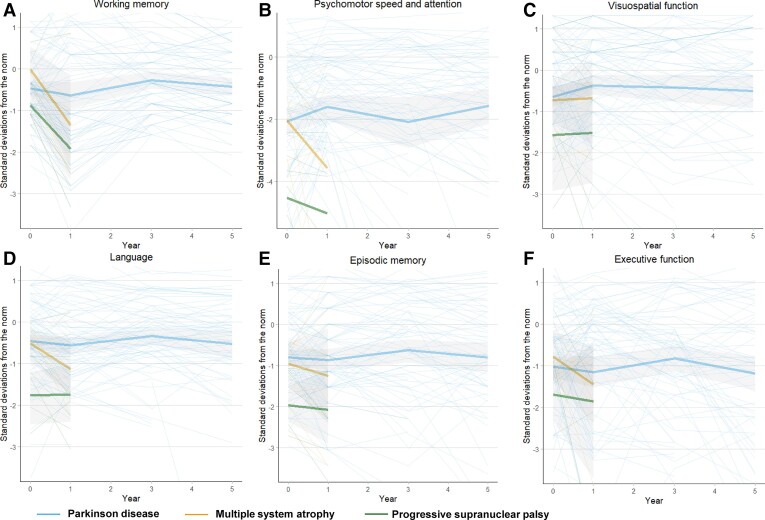
Figure 2.
Dysfunction in specific cognitive domains in idiopathic parkinsonism. Cognitive test results in each cognitive domain (A, working memory; B, psychomotor speed and attention; C, visuospatial function; D, language; E, episodic memory; F, executive function) measured in SDs from the scores of the HCs (norm) at baseline. Test results are shown both for individuals (thin lines) and for diagnostic group means (thick lines), as the mean is affected by selection bias over time. Difference between HCs and (i) Parkinson disease (for A, mean SD: −0.49, P = 0.002; B, mean SD: −2.19, P < 0.001; C, mean SD: −0.67, P = 0.003; D, mean SD: −0.50, P = 0.004; E, mean SD: −0.87, P < 0.001; F, mean SD: −1.13, P < 0.001), (ii) MSA (for A, mean SD: −0.30, n.s.; B, mean SD: −2.56, P < 0.001; C, mean SD: −0.46, n.s.; D, mean SD: −0.50, n.s.; E, mean SD: −0.84, P = 0.033; F, mean SD: −0.98, P = 0.003) and (iii) PSP disease (for A, mean SD: −1.15, P = 0.002; B, mean SD: −4.44, P < 0.001; C, mean SD: −1.74, P < 0.001; D, mean SD: −1.65, P < 0.001; E, mean SD: −1.85, P < 0.001; F, mean SD: −1.56, P < 0.001) is between-groups mean differences estimated by linear mixed models. In the figure, the mean is only shown until 1 year for MSA and PSP because of few datapoints beyond this time point. For tests included in each domain, see Supplementary material. See also Table 2. Grey area, 95% CI; Year 0, baseline; n.s., non-significant.