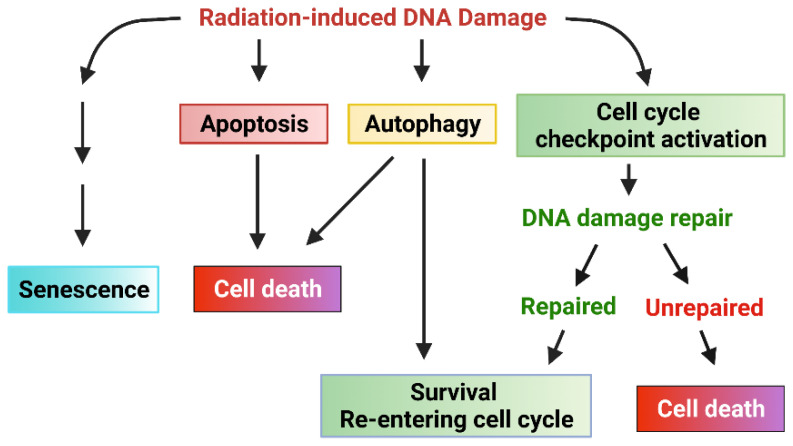
Figure 1.
Cellular response to radiation-induced DNA damage. Ionizing radiation (IR) induces DNA damage in cancer cells in the form of either single-strand breaks (SSB) or double-strand breaks (DSB). DNA damage sensed by cells results in various cellular responses: senescence, apoptosis, autophagy, cell cycle arrest, and DNA repair. Signaling pathways that promote cell cycle checkpoint activation/DNA repair and inhibition of apoptosis can protect cancer cells from IR-induced cytotoxicity, promoting survival and the subsequent radiation resistance of cancer cells.