Fig. 2.
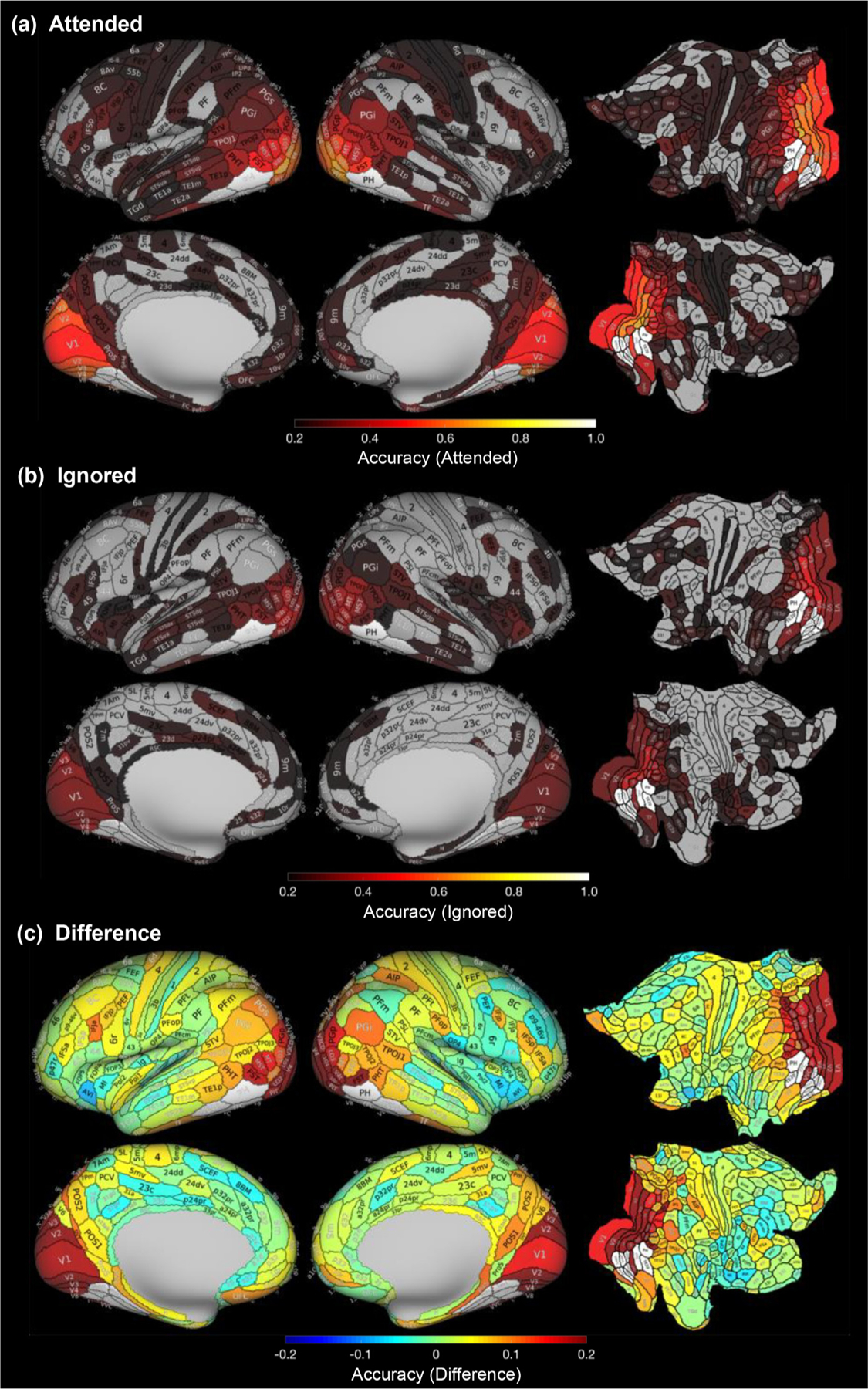
Classification of category information is higher for attended than ignored stimuli. Mean classification accuracy (proportion of object categories correctly classified) across 21 subjects and 5 object categories for (a) attended and (b) ignored categories. Maps are shown for the inflated lateral (top) and medial (bottom) cortical surfaces as well as flattened views (right) and are thresholded at chance level. That is, gray ROIs represent those with classification accuracy below chance level (0.2). (c) Mean difference in classification accuracy between attended and ignored conditions. Statistical significance values of the difference for each Glasser ROI are shown in Supplementary Figure 6a. White indicates Glasser ROIs overlapping VTC category-selective ROIs which were excluded from analyses.
