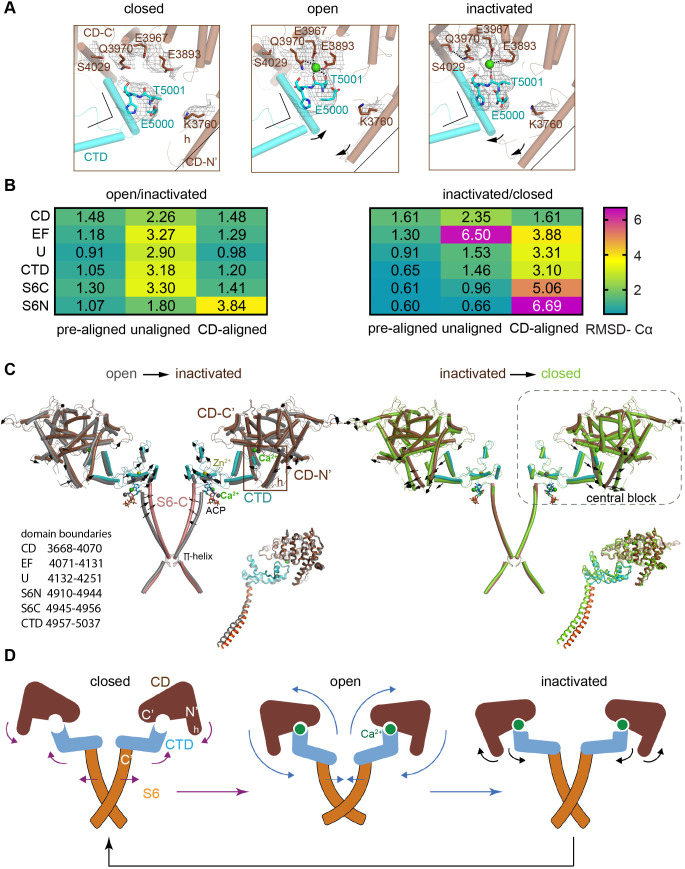
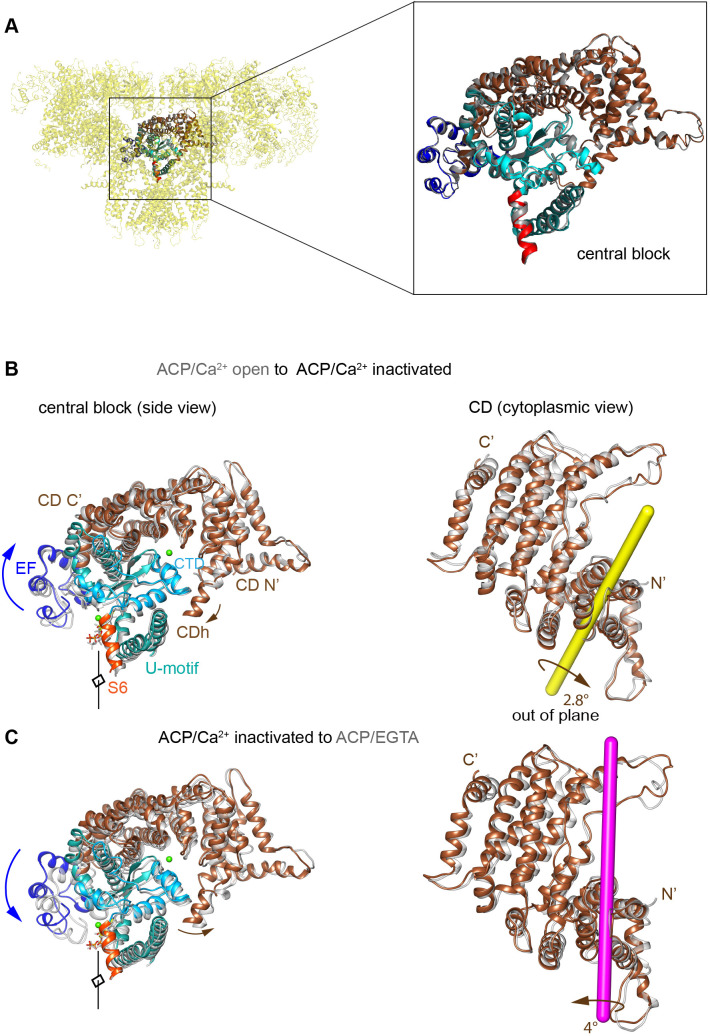
Figure 2. Inactivation of RyR1 involves out-of-plane rotation of the central block and rearrangement around the Ca2+ activation site.
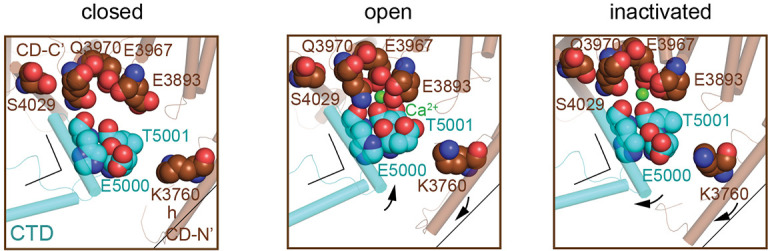
(A) The high-affinity Ca2+-binding site in the CD/CTD interface with density around the Ca2+ site contoured at 4σ. Contacts within 2.8 Å from Ca2+, as well as additional contact Gln3970-Ser4029 within 3.6 Å, are represented by dashed lines. Channel axis is on the left. During the transition from open to inactivated conformations, the CD/CTD block tilts around the Ca2+-binding site such that the protruding fourth helix of the CD (h) and connected CTD tilt inward, while the CD-C′ tilts upward and away from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) membrane – with Gln3970 separating from Ca2+ by ~6 Å. Arrows and stationary reference lines illustrate the conformational changes undergone with respect to the panel on the left. The region represented relative to the channel is highlighted with a square in panel (C). See Figure 2—figure supplement 1 for the corresponding space-filling representation. (B) Heat map showing Cα-backbone root mean square deviation (RMSD) (in Å) between domain pairs from respective conformations after aligning them (pre-aligned), in their native conformation (unaligned), and after aligning the protomers through their respective CD (CD-aligned). The RMSD difference between unaligned and pre-aligned represents the change caused by domain relocation. (C) Overlaid structures of the CD-CTD-S6 domains in different conformations; only two protomers shown for clarity. Left: in the transition from RyR1-ACP/Ca2+ open (gray) to RyR1-ACP/Ca2+ inactivated (colored), the CD-CTD block, ‘connected’ by Ca2+ coordination, undergoes an out-of-plane rotation around the Ca2+-binding site that pushes S6C′ toward the pore axis, closing the channel. Right: in the transition from RyR1-ACP/Ca2+ inactivated (colored) to RyR1-ACP/EGTA (green), Ca2+ unbinding disconnects the CD from the CTD. Structures at the bottom right of each panel show the comparison of the CD-CTD-S6C′ of the central block after forcing superimposition of their respective CDs. Residue boundaries for relevant domains are specified. (D) Schematics of the conformational changes from RyR1-ACP/EGTA (closed), to RyR1-ACP/Ca2+ open, to RyR1-ACP/Ca2+ inactivated. Activation, where Ca2+ binds to the high-affinity site, is required prior to inactivation. The CD-protruding fourth helix (3753–3769) is indicated by ‘h.’ Colored arrows indicate the conformational change toward the following structure.
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Reorganization of the high-affinity Ca2+-binding site at the CD/CTD interface under different conditions.