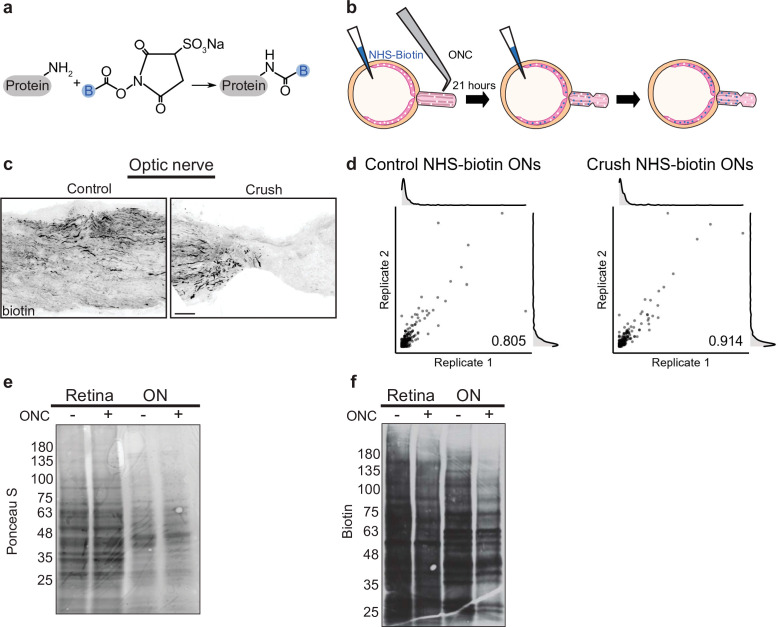
Figure 1. Pulsed N-hydroxysuccinimidobiotin (NHS-biotin) labels and quantifies protein transport after injury.
(a) NHS-biotin (biotin group in blue) reacts with primary amines adding a defined mass shift to tagged proteins. (b) NHS-biotin (blue) was injected before injury with a repeat injection 21 hr later. Biotinylated proteins in retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) transport down intact RGC axons in the optic nerve. The retinas and optic nerves were collected for tissue processing after 3 hr. (c) No biotinylated proteins were detected by immunofluorescence distal to the crush site. Scale bar, 100 µm. (d) Pearson’s R correlation of proteomic replicates of control or optic nerve crush (ONC) samples (R = 0.805 and 0.914, respectively). (e) Ponceau S stain of protein from biotinylated retinas and optic nerves, with and without ONC, showing equivalent total protein. Molecular ladder labeled on left of blot. (f) Western blot of the same samples run in parallel, probing for biotin. ONC decreased biotinylated proteins to a greater extent in ON compared to retina. Molecular ladder labeled on left of blot.