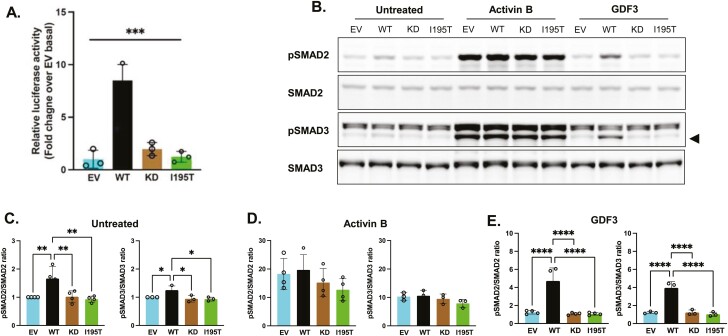
Figure 4.
Functional impact of ACVR1C I195T variant on Smad signaling. A, HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with ACVR1C expression constructs and their receptor components, along with firefly and Renilla luciferase expression plasmids. Firefly luciferase activity was normalized to Renilla activity and the luciferase activity in nonstimulated cells transfected with empty vector (EV) was set to 1. A constitutively active (CA) ACVR1C variant T194D and a kinase-deficient (KD) variant K222R were included for comparison. Results from 3 independent experiments are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was evaluated by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey post hoc test for multiple comparisons between pairs. WT, wild-type ACVR1C. B to D, HEK293T cells transfected with plasmids containing EV, WT ACVR1C, KD ACVR1C, or I195T ACVR1C were treated for 30 minutes with activin B (25 ng/mL) or growth and differentiation factor 3 (GDF3; 500 ng/mL), and B, SMAD signaling was determined via Western blotting. Black triangle indicates pSMAD3 band. SMAD activation was quantified by the ratio of phospho-SMAD2 to total SMAD2 protein and phospho-SMAD3 to total SMAD3 protein for each condition: C, untreated; D, activin B; and E, GDF3. Data are expressed as relative pSMAD:SMAD ratios normalized to untreated EV controls. Three or 4 independent experiments were combined for analysis, and differences between ACVR1C transfection groups were determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test for multiple comparisons between pairs. ***P less than .001; **P less than .01; *P less than .05; ns, not significant.