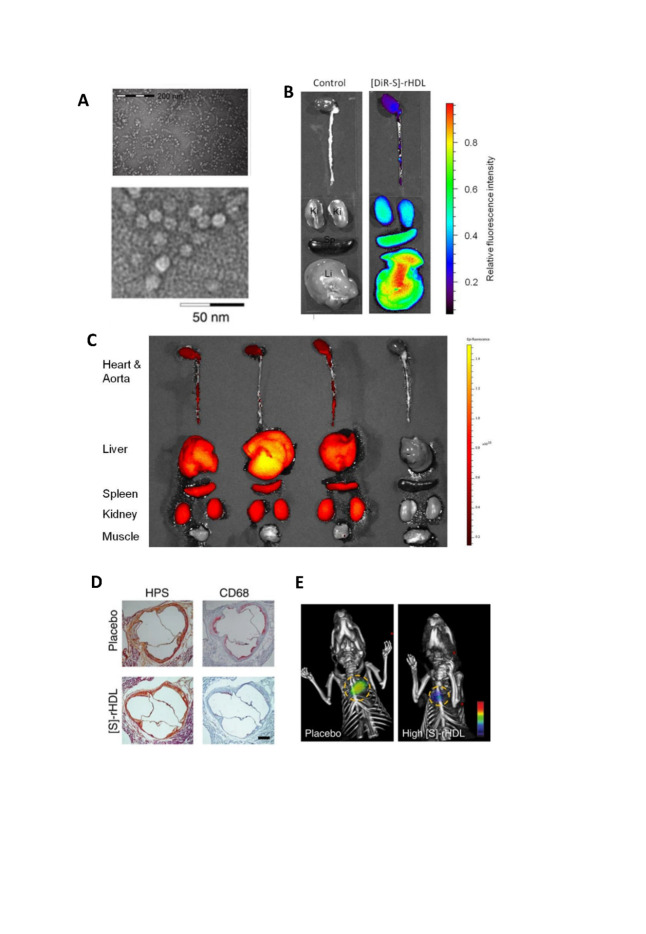
Figure 3.
The strutural features of reconstituted high-density lipoprotein (rHDL) that promote targeted treatment. (A) Negative staining TEM image showed the typical disk-like morphology of rHDL. (B) Mice were intravenously injected with [DiR-S]-rHDL nanoparticles [rHDL fabricated with stain], and organs were imaged with NIRF 24 hours after the injection. Liver has the highest retention of DiR, followed by spleen, and kidney has the lowest retention. (C) Three mice were intravenously injected with [DiR-S]-rHDL (left three) and one control mouse was not injected (on the right). Organs were imaged with NIRF 24 hours after the injection. While heart, aorta, liver, spleen, and kidney tissue all took up nanoparticles, muscle tissue did not. (D)Typical histology images of the aortic sinus area from a mouse in the placebo group and a mouse in the high-dose [S]-rHDL group show that the mean plaque area is similar, while the plaque macro-phage content is notably smaller in the [S]-rHDL group. (E) FMT-CT molecular im-aging of protease activity revealed that high-dose [S]-rHDL treatment significantly reduced the inflammation levels in the aortic roots of live apoE-KO mice with advanced atherosclerosis as compared with placebo. The yellow circles indicate the aortic root area. All figures were cited from reference [70].