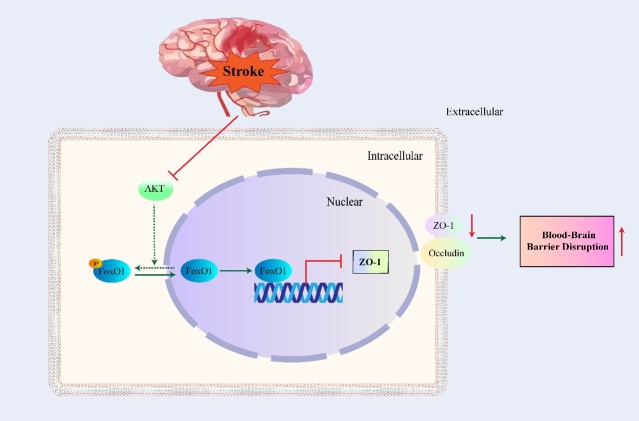
Figure 3.
Schematic model for role of FoxO1 in BBB disruption. After stroke, activation of Akt pathway is inhibited. Then the phosphorylation of FoxO1 is suppressed which further leads to nuclear translocation and activation of FoxO1. Activation of FoxO1 results in downregulation of ZO-1 at the transcriptional level, which further leads to increased BBB disruption. The solid line represents the pathway that occurs after stroke, and the dotted line represents the pathway suppressed after stroke.