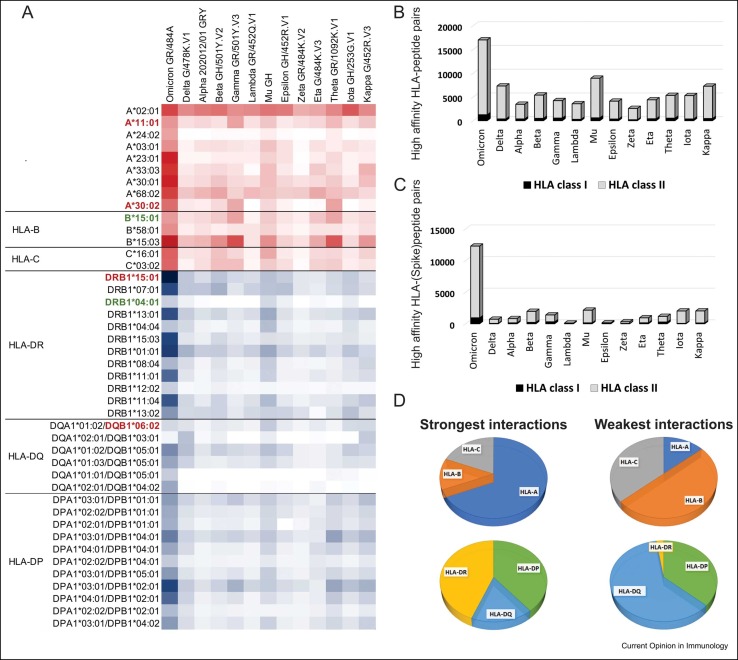
Figure 3.
Peptides from different SARS-CoV-2 variants have distinctive affinities for HLA molecules. Data extracted from T-cell COVID-19 Atlas [35] determined using netMHCpan-4.1 and netMHCIIpan-4.0 [34]. The affinity scores were not directly compared across genes; all plots show absolute numbers of strong or weak interactions. (a) Most relevant HLA–peptide interactions across all SARS-CoV-2 variants. The color intensity in each box represents the absolute number of strong interactions (IC50 affinity ≤ 50 nM) predicted between specific HLA allotypes and the peptides from each SARS-CoV-2 variant, varying from white (zero strong interaction) to dark red (67 strong interactions; HLA class I) and dark blue (656 strong interactions; HLA class II). We included only the allotypes with the strongest interactions based on the affinity scores and excluded those HLA variants observed in low frequencies (f<0.05) in three reference populations from 1000 Genomes Dataset (CEU, YRI, and CHB) [39]. Allotypes from each locus are ordered from the most frequent to the least frequent, according to the maximum frequency observed in these three reference populations. HLA variants that have been previously associated with COVID-19 are shown in bold, with those associated with risk or severe disease shown in red and those associated with asymptomatic or mild infection in green. Omicron is the variant predicted to exhibit the highest number of peptides strongly interacting with HLA class I and class II molecules, considering the mutations in (b) all viral proteins and also (c) only the Spike protein. (d) Distribution of allotypes predicted to have strong and weak interaction for SARS-CoV-2 stratified by locus. On the left, the plot represents the stratification of the top 30% of the strongest interactions with SARS-CoV-2 peptides; on the right, the distribution of allotypes in the bottom 30%, representing the HLA molecules with weak or no interaction with SARS-CoV-2 peptides.