Figure 3.
IGHD1-26 is enriched among SARS-CoV-2 S2 antibodies
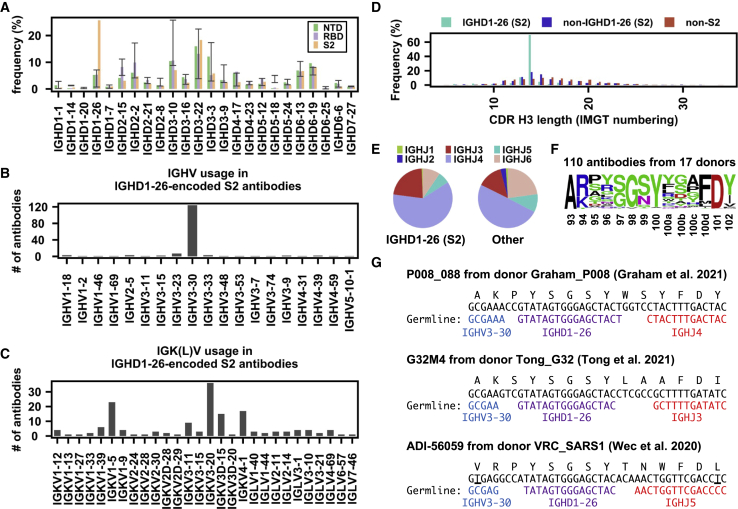
(A) The IGHD gene usage in NTD, RBD, S2 antibodies is shown. Error bars represent the frequency range among 26 healthy donors.
(B and C) (B) IGHV gene usage and (C) IGK(L)V gene usage among IGHD1-26 S2 antibodies is shown (n = 157).
(D) The distribution of CDR H3 length (IMGT numbering) in IGHD1-26 S2 antibodies (n = 157), non-IGHD1-26 S2 antibodies (n = 533), and non-S2 S antibodies (n = 5,090) are shown.
(E) The IGHJ gene usage among IGHD1-26 S2 antibodies (n = 157) and other S antibodies with well-defined epitopes (n = 5,623) is shown.
(F) The CDR H3 sequences for IGHD1-26 S2 antibodies (n = 110) are shown as a sequence logo.
(G) Amino acid and nucleotide sequences of the V-D-J junction are shown for three IGHD1-26 S2 antibodies (Graham et al., 2021; Tong et al., 2021; Wec et al., 2020). While P008_088 and G32M4 were from SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals, ADI-56059 was from a SARS-CoV survivor. Putative germline sequences and segments were identified by IgBlast (Ye et al., 2013) and are indicated. Somatically mutated nucleotides are underlined. Intervening spaces at the V-D and D-J junctions are N-nucleotide additions. See also Tables S1 and S2.