Fig. 9.
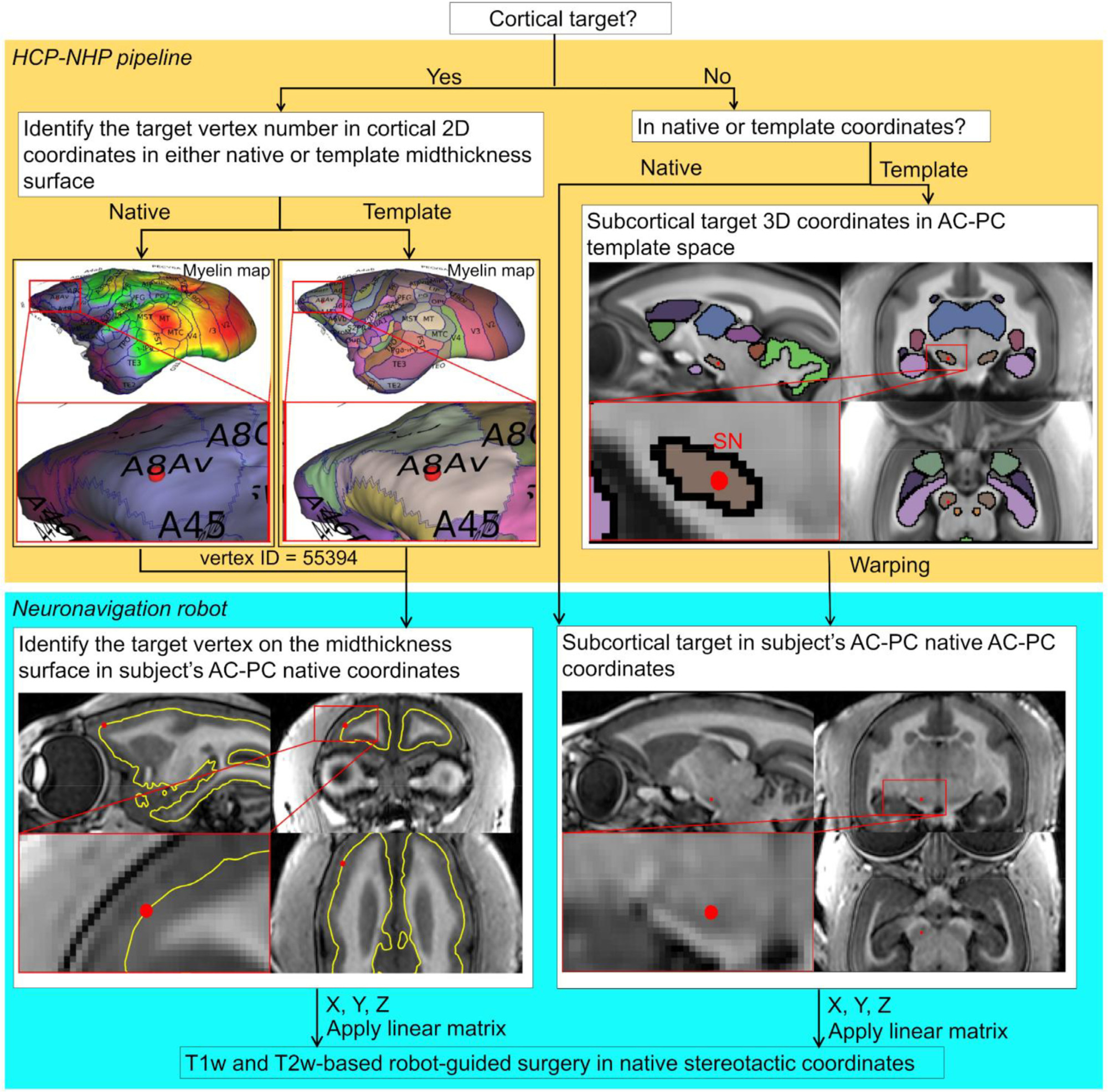
Neuronavigation strategy for cortical and subcortical targets in marmosets. For cortical surgery, the target is first identified on the vertex in cortical 2D coordinates (in either native or template midthickness surface). Next, the 3D coordinates corresponding to the vertex number of interest are read in the subject’s AC-PC native coordinates. For subcortical surgery, the target is identified in the 3D coordinate system (either in template or native coordinates). When the template coordinate system is used, the target’s 3D coordinates are warped to the subject’s AC-PC native coordinates. The robot-guided neurosurgery utilises these 3D coordinates by transforming from subject’s AC-PC native to the stereotactic coordinates. Study ID: (MRI: A17051101).
