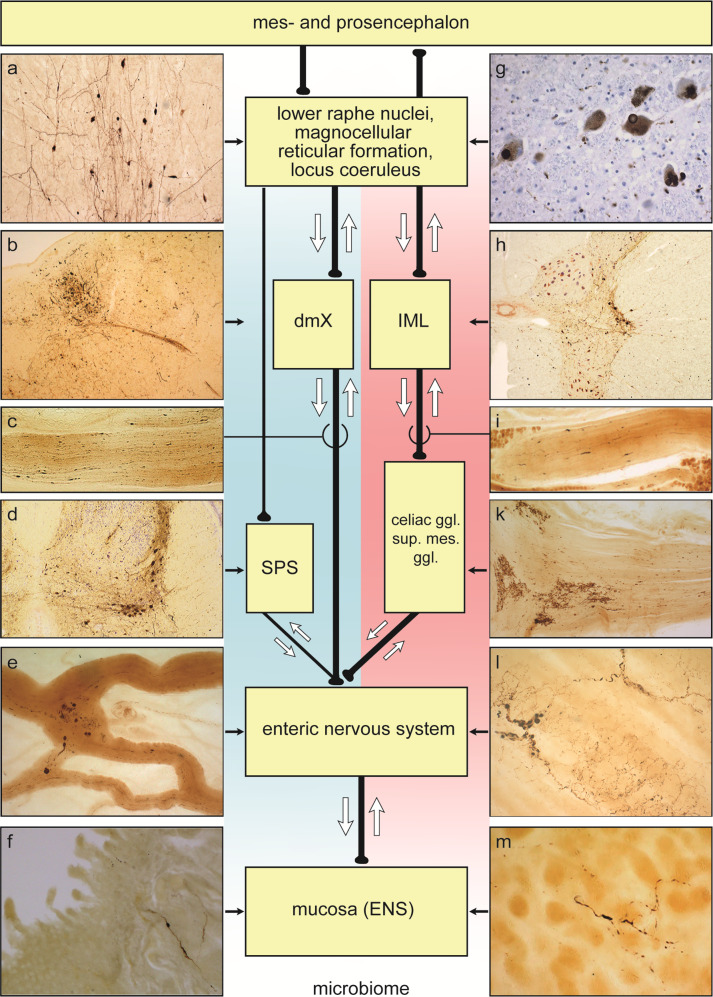
Fig. 1. Diagram showing possible bidirectional (white arrows) parasympathetic (blue background) and sympathetic (pink background) pathways along which pathological α-synuclein propagation in ILBD and PD could occur between the periphery, including the ENS, and the CNS.
Retrograde: parasympathetic (distal esophagus/stomach → pN. X → dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve, dmX); parasympathetic (appendix vermiformis → RIM → pN. X → dmX); parasympathetic (descending colon and further distal → ganglion pelvicum → SPS preganglionic neurons → lower brainstem level-setting nuclei); sympathetic (distal esophagus/stomach → prevertebral celiac ganglion postganglionic neurons → IML preganglionic neurons → lower brainstem level-setting nuclei). Alternatively, anterograde: parasympathetic (dmX → pN. X → distal esophagus/stomach); parasympathetic (lower brainsteim level-setting nuclei → SPS preganglionic neurons → prevertebral postganglionic ganglion pelvicum → descending colon and portions further distal); sympathetic (appendix vermiformis → RIM → prevertebral SMG postganglionic neurons → Nn. splachnici → IML preganglionic neurons → lower brainstem level-setting nuclei).Abbreviations: pN. X peripheral vagus nerve, dmX dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve, IML intermediate mediolateral nucleus, SPS sacral parasympathetic nucleus, RIM root of the small intestine mesentery, sup. mes. ggl. superior mesenteric ganglion. The level-setting nuclei consist of the lower raphe nuclei, magnocellular nucleus of the reticular formation, and locus coeruleus81. The RIM contains parasympathetic and sympathetic fibers innervating the upper GIT extending from the proximal jejunum to the distal ileum, thereby making it another potentially useful structure for neuropathological diagnosis of the existence of LP in the small intestine61,232. Illustrations showing LP in a–m are not to scale: a great raphe nucleus. b dmx and intramedullary N. X. c pN. X at level of the carotid bifurcation. d SPS. e Gastric cardia, Auerbach plexus, tangential section. f Jejunum, Meissner (submucous) plexus, transversal section. g Locus coeruleus. h IML. i Splanchnic nerve at the level of the celiac ganglion. k Celiac ganglion. l Distal esophagus, Auerbach plexus, tangential section. m Gastric cardia, Meissner (submucous) plexus, tangential section. LP within the lamina propria reach the mucosa near gastric glands. Syn-1 immunohistochemistry (BD Biosciences, Eysins, Switzerland) in 100–150 µm sections.