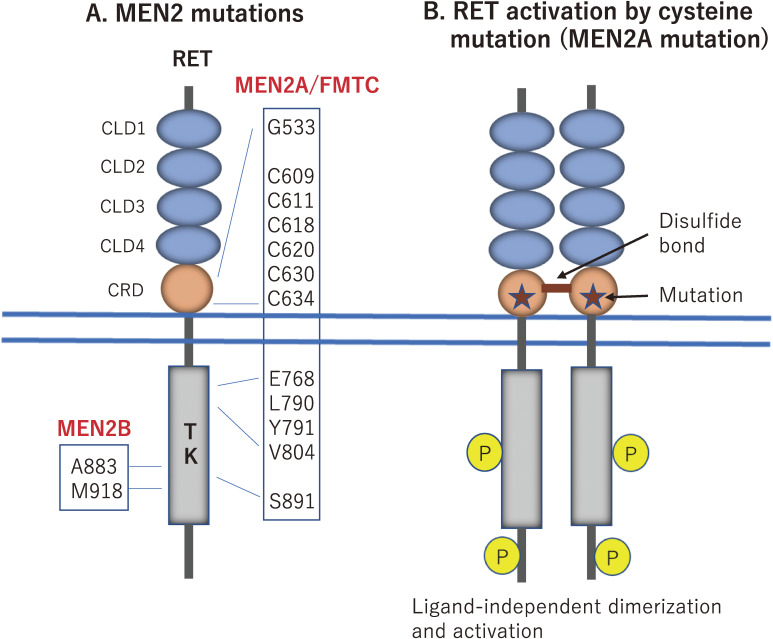
Figure 6.
Germline RET mutations in MEN2. A. The majority of MEN2A mutations (>95%) are identified in one of six cysteine residues (codons 609, 611, 618, and 620 in exon 10 and codons 630 and 634 in exon 11) in the cysteine-rich domain (CRD) of the RET extracellular region. In addition to cysteine substitutions, FMTC mutations are frequently found at noncysteine residues in both the extracellular and intracellular regions. The M918 mutation is detected in >95% of MEN2B patients. B. Mechanism of RET activation by cysteine mutations. When a cysteine residue is replaced with another amino acid in MEN2A/FMTC (indicated by stars), mutant RET proteins form ligand-independent covalent dimerization, resulting in constitutive activation.