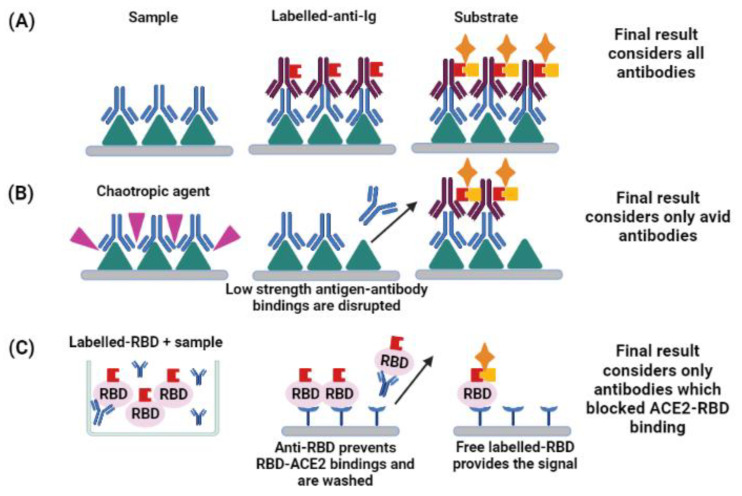
Figure 2.
Differences in non-functional and functional enzyme-linked assays. While non-functional assays (A), like regular ELISA, detect antibodies that are bound with the antigen, functional assays detect antibodies regarding specific characteristics. (B) Avidity assays consist in adding a chaotropic agent that will disturb the epitope-paratope interaction, disrupting weak bindings. Only avid antibodies keep attached and are revealed in the final result. Both A and B assays should consider which antigen of SARS-CoV-2 was used to coat the plate (e.g., RBD, Spike protein, Nucleocapsid protein) and the specificity of the anti-Ig used for detection (e.g., anti-IgA, anti-IgM, anti-IgG). For quantitative results, the higher the signal, the higher the antibody quantity. (C) Surrogate-virus neutralization assays, based on a competitive ELISA, allow the interaction between labelled-RBD and the sample, after that, the mix is incubated in ACE-2 coated plates. Therefore, free-RBD binds to the plate and complexes antibody-labelled-RBD, which cannot bind with it, are washed. It should be noted that the assay considers all anti-RBD antibodies, despite its Ig class. For quantitative results, the lower the signal, the higher is the antibody quantity. (figure created with BioRender).