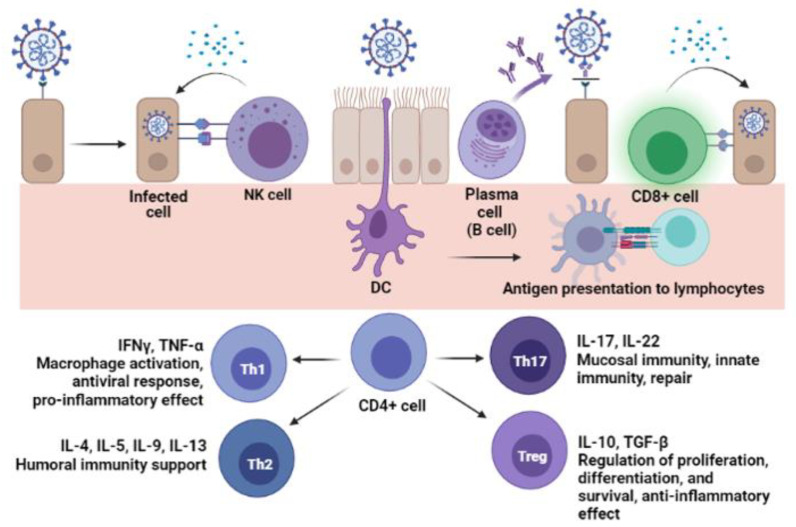
Figure 3.
Immune cells and SARS-CoV-2 infection. SARS-CoV-2 is internalized after the RBD-ACE2 interaction. Natural-killer (NK) cells can identify infected cells and kill them after the release of cytotoxic proteins (like perforin and granzyme). Dendritic cells (DC) are responsible for capture, processing, and presentation of pathogen to lymphocytes, to assemble the adaptive immune response. After activation and antigen presentation, plasma (B) cells produce and release antibodies that, for example, can neutralize the virus by inhibition of RBD-ACE2 interaction; while cytotoxic T cells (CD8+ cell) recognize infected cells and kill it by releasing cytotoxic proteins. Auxiliary T cells (CD4+ cell) differentiate to certain T helper (Th) types, releasing cytokines that modulate the immune environment, supporting different arms of response. A well-orchestrated immune response is necessary to control the infection without harming the host and the products secreted by cells (e.g., proteins, cytokines, immunoglobulins) can be enzyme-linked detected. (figure created with BioRender).