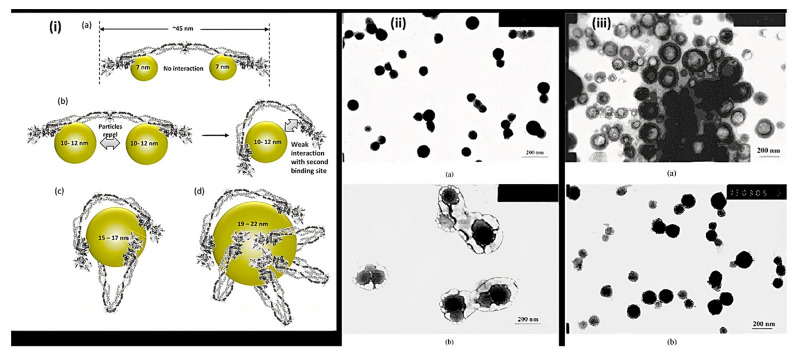
Figure 4.
Representation of (i) binding of fibrinogen with PAA/Au nanoparticles (a) Binding of 7 nm nanoparticle to fibrinogen revealing each protein molecule accommodated two nanoparticles (b) 10–12 nm-sized nanoparticles prevent the binding of two particles to each fibrinogen due to the flexibility of fibrinogen at E domain of protein resulting the contact of second binding site with the nanoparticle (c,d) Larger nanoparticles (15–22 nm) can accommodate multiple fibrinogen molecules due to the larger surface area (ii) TEM of PAA-CS nanoparticles at (a) pH = 4.5 and (b) at pH = 7.4. (iii) Morphology of PAA-CS nanoparticles synthesized by the various processes at 4.5: (a) CS dropping into PAA solution; (b) PAA dropping into CS solution, (Reprinted from Refs. [81,83] with permission).