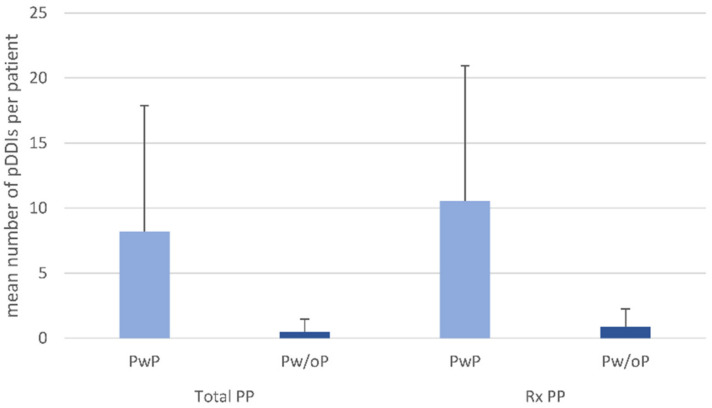
Figure 1.
Average number of pDDIs per patient with MS, stratified by PP status and type of PP. The patients were classified by PP status according to total PP (intake of at least five drugs of any kind) and Rx PP (intake of at least five drugs only available on prescription). Standard deviations are displayed as error bars. The average number of pDDIs was higher in PwP compared with Pw/oP, for both total PP (8.2 ± 9.7 versus 0.5 ± 1.0) and Rx PP (10.5 ± 10.4 versus 0.9 ± 1.4). MS—multiple sclerosis; pDDI—potential drug–drug interaction; PP—polypharmacy; PwP—patients with polypharmacy; Pw/oP—patients without polypharmacy; Rx—only available on prescription.