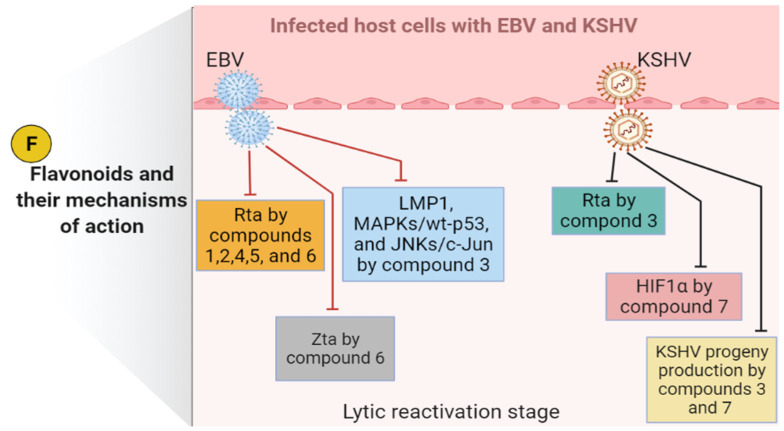
Figure 3.
Flavonoids and their mechanisms of action against EBV and KSHV during the lytic reactivation stage of the life cycle. The blunt-end arrows indicate inhibition/downregulation. EBV, Epstein–Barr virus; F, flavonoids (luteolin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (1), apigenin-7-O-[β-D-apiofuranosyl (1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside (2), epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG, 3), protoapigenone (4), protoapigenone 1′-O-isopropyl ether (5), apigenin (6), and hesperetin (7)); HIF1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; JNKs/c-Jun, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases/c-Jun; KSHV, Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus; LMP1, latent membrane protein 1; MAPKs/wt-p53, mitogen-activated protein kinases/wild-type p53; Rta, replication and transcription activator; Zta, an immediate-early gene.