Figure 5.
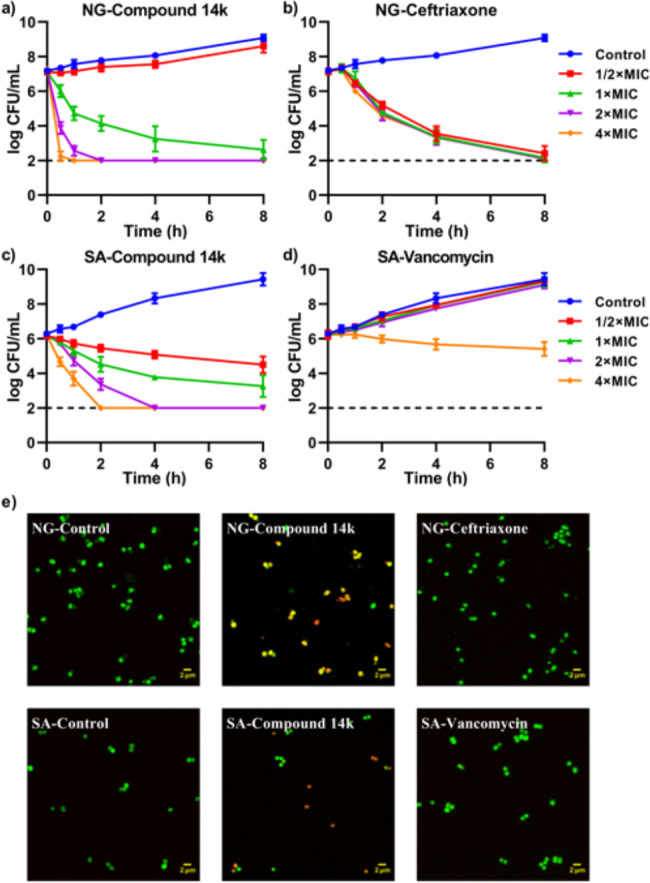
Bactericidal activity of compound 14k against Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Staphylococcus aureus. Bacterial suspensions of N. gonorrhoeae strain ATCC 49226 (NG) and S. aureus strain ATCC 25923 (SA) in GC broth supplemented with 1% Vitox were incubated with compound 14k or the control antimicrobials ceftriaxone (NG) and vancomycin (SA) at 4×, 2×, 1×, and 1/2× the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) or the vehicle control. Samples were taken in a time series for CFU determination or live/dead staining. (a) Survival curves of N. gonorrhoeae after exposure to compound 14k (1 × MIC: 2 μM). (b) Survival curves of N. gonorrhoeae after exposure to ceftriaxone (1 × MIC: 0.008 μM). (c) Survival curves of S. aureus after exposure to compound 14k (1 × MIC: 4 μM). (d) Survival curves of S. aureus after exposure to vancomycin (1 × MIC: 7 μM). Survival curves represent the mean and SD of three biological independent repeats. (e) Live/dead staining of N. gonorrhoeae and S. aureus after exposure to the vehicle control, compound 14k, or control antibiotics ceftriaxone and vancomycin at 1× MIC for 1 h. Viable bacteria are stained with SYTO 9 (green), whereas dead bacteria are stained with propidium iodide (red) or with both SYTO 9 and propidium iodide (yellow).
