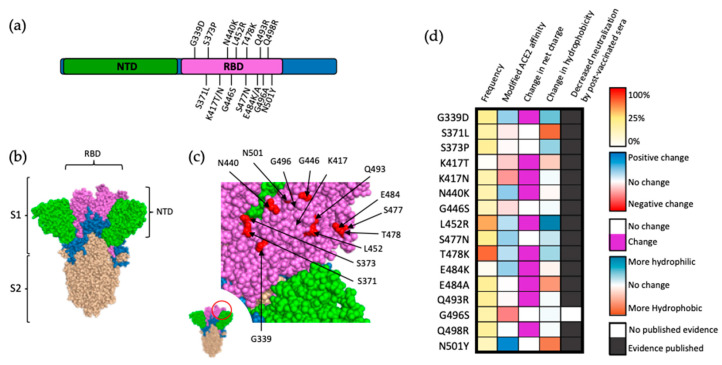
Figure 3.
Mutations within the RBD of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. (a) Visual representation of mutations within the RBD (magenta) of SARS-CoV-2 spike. Notably, 15 out of the 32 amino acid substitutions in the spike protein are localized in the RBD. (b) Structural location of SARS-CoV-2 S subunits. (c) Close-up view of RBD (magenta) and VOC-occurring mutations (red). (d) Frequency, effect on ACE2 affinity, modification of charge at physiological pH, alterations in hydrophobicity at pH 7, and direct evidence of decreased neutralization by postvaccinated sera for mutations within the RBD of S protein. Frequency is presented as a percentage of reported SARS-CoV-2 genomes logged within the GISAID database, as a notion of fitness advantage. Alteration in ACE2 affinity based on data by Starr et al. [21], with mutations that increase ACE2 affinity in blue and mutations negatively impacting ACE2 affinity in red. Frequency represented as a percentage of reported SARS-CoV-2 genomes logged within the GISAID database retrieved 10 March 2022. Alterations in hydrophobicity based on previously established values [23]. Alterations in residue charge based on standard calculations at physiological pH.