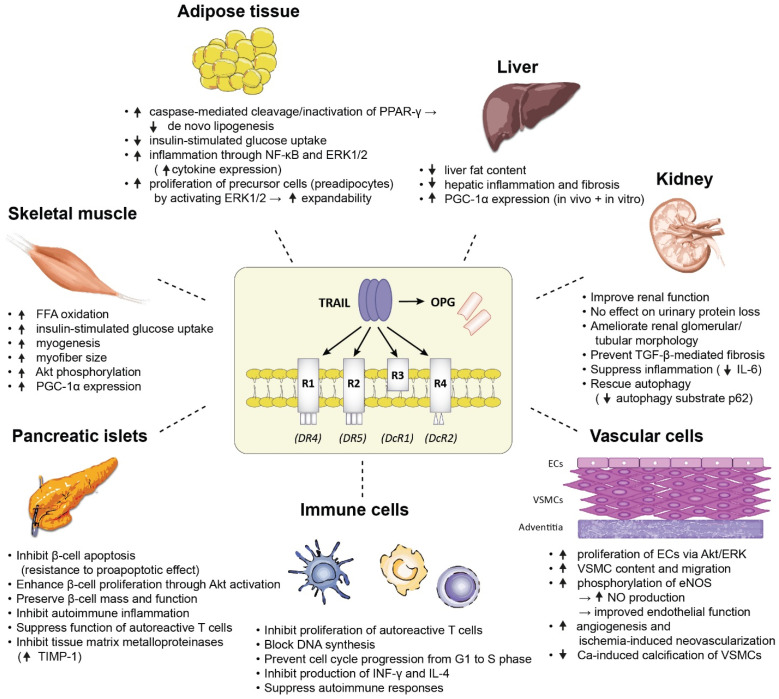
Figure 2.
A summary of the major biological effects of TRAIL on a variety of tissues which are pathogenetically involved in the development of diabetes, as demonstrated in animal and in vitro mechanistic studies. Abbreviations: Akt: protein kinase B; ECs: endothelial cells; eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide synthase; ERK1/2: extracellular signal regulated kinases 1 and 2; FFA: free fatty acid; IL-4: interleukin-4; IL-6: interleukin-6; INF-γ: interferon-γ: NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa B; NO: nitric oxide; PGC-1α: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ co-activator-1α; PPAR-γ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-β; TIMP-1: tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1; VSMCs: vascular smooth muscle cells.