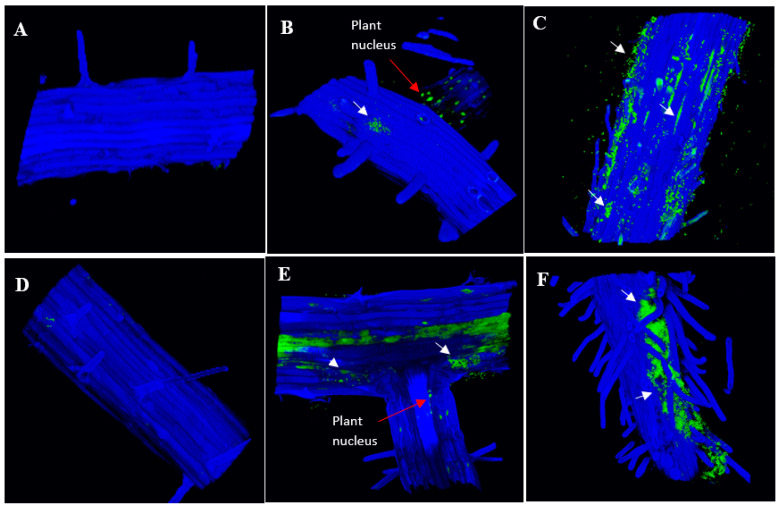
Figure 4.
IAA-producing strains that inhibit root length are abundant on wild-type root tissue. A 3D reconstruction from confocal microscopy of wild-type Arabidopsis roots upon treatment with (A) no bacteria, (B) non-IAA-producing Bacillus RU3D, (C) IAA-producing Microbacterium RU1A, (D) IAA-producing Microbacterium RU33B, (E) IAA-producing Herbaspirillum RU5E, and (F) IAA-producing Azospirillum baldaniorum Sp245. The microscopy channels are blue (calcofluor white used to stain the cell wall) and green (SYBR Gold DNA used to stain the nuclei and bacteria). White arrows indicate bacteria location based on the size of the DNA-stained spots. Bacteria are shown as green spots that are smaller in size to plant nuclei.