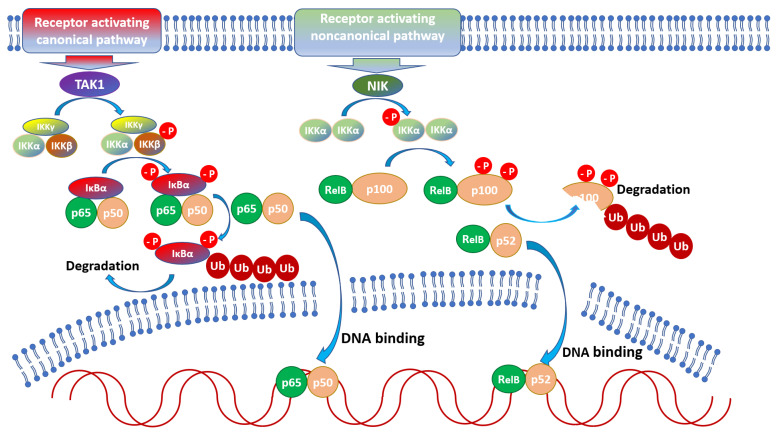
Figure 1.
Schematic model of NF-κB activation through canonical and non-canonical pathways. Canonical activation involves TGF-β activated kinase-1 (TAK1) which phosphorylates Inhibitory Kappa B Kinase β (IKKβ) complexed with IKKα and IKKγ (NEMO). This leads to phosphorylation of the α Inhibitor of κB (IκBα), its detachment from the p56/p50 dimer, ubiquitination, and proteasomal degradation. Released p65/p50 dimer migrates to the nucleus and binds to DNA sequences leading to transcription of appropriate genes. During the noncanonical pathway, NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) phosphorylates the IKKα dimer which phosphorylates p100 leading to its disruption and release of the RelB/p52 dimer. The dimer migrates to the nucleus and regulates the transcription of particular genes.